|
Blood Fats
Fat is a source of energy. It carries some vitamins around the body.
It is used to make hormones and cell membranes, to protect organs and
to lubricate some moving body parts. However, too much fat in the blood
increases the risk of heart disease or pancreatitis.

| Excess body fat is linked to major physical
threats like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
(Three out of four prople die of either heart
disease or cancer each year; according to the
National Health and Nutrition Examination survey,
approximately 80 percent of those deaths are
associated with life-style factors, including
inactivity.) |
Triglycerides are the most common form
of fat in the body. Cholesterol is another form of
fat. In order for fats to be carried in the blood,
they are wrapped in protein molecules. These bundles
of protein-wrapped fat are called lipoproteins.
Lipoproteins come in different sizes. Smaller ones
are called low-density lipoproteins (LDL) or very-low-density
lipoproteins (VLDL). These molecules carry fats from
the liver to other parts of the body. Too much LDL
or VLDL can cause fat to build up on the walls of your
arteries. This can reduce the oxygen supply to your
heart muscle and cause heart disease or a heart attack.
| "Obese
people also tend to have high cholesterol
levels, making them more prone to arteriosclerosis,
a narrowing of the arteries by deposits of
plaque. This becomes life-threatening when
blood vessels become so narrow or blocked that
vital organs like the brain, heart or kidneys
are deprived of blood. Additionally, the narrowing
of the blood vessels forces the heart to pump
harder, and blood pressure rises. High blood
pressure itself poses several health risks,
including heart attack, kidney failure, and
stroke. About 25 percent of all heart and blood
vessel problems are associated with obesity. " Who
is obese? |
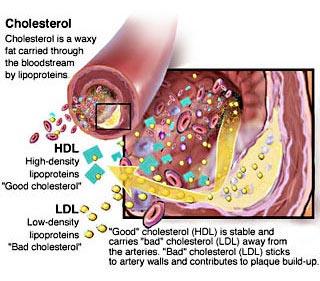
Larger lipoproteins are called high-density
lipoproteins (HDL). These are called "good" lipoproteins
because they remove fats from your arteries and return
them to the liver for more processing. High levels
of HDL seem to protect people from heart disease.
Blood fats are measured as the amount (in milligrams)
contained in one tenth of a liter (a deciliter) of
blood, or mg/dL.
Cholesterol is
a waxy, fat-like material that is found in all parts
of the body.
It comes from two sources: our liver produces it, and we consume it in
meat
and dairy products, if elevated in the blood, it has been associated
with heart disease.
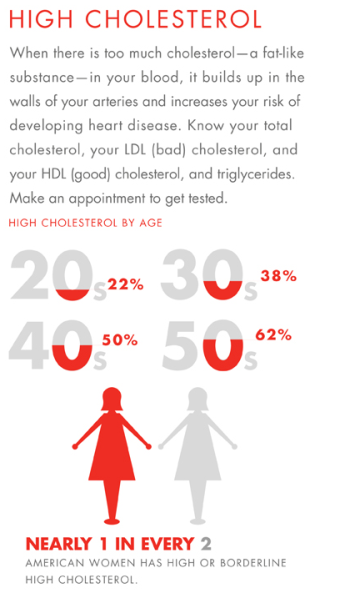
Risks: High
levels of fat are associated with disorders such as
arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis, heart attack and
stroke.

Total Cholesterol: A
high cholesterol in
the blood is a major risk factor for heart and blood
vessel disease. Cholesterol in itself is not all bad,
in fact, our bodies need a certain amount of this substance
to function properly. However, when the level gets
too high, vascular disease can result. A total cholesterol
of less than 200, and an LDL Cholesterol of 100 or
less is considered optimal by the National Heart, Lung,
and Blood Institute. The levels that your doctor will
recommend depend upon whether you are at high risk
for cardiovascular disease.
As the level of blood cholesterol increases,
so does the possibility of plugging the arteries due
to cholesterol plaque build-up. Such a disease process
is called "hardening of the arteries" or
atherosclerosis. When the arteries feeding the heart
become plugged, a heart attack may occur. If the arteries
that go to the brain are affected, then the result
is a stroke.
Whenever we put up information on alternative
treatments that have not been properly/Scientifically
tested, we receive a few angry emails. They say" we
are trying to prevent people with Dis-ease from
getting effective treatment". That is really
not what we wish to do.
What concerns us is that potential treatments,
like these in the following pages, ar eeither
ignored or ridiculed by conventional health
,and often
sold for a great deal of money. People with
Dis Ease can be vulnerable. It is understandable
that patients or relatives will try anything
if they
think it might work. And that people really
do
want to believe that they work..
Our message is Be careful, Make sure you look
into all the information that is available
Talk to your doctor before you consider any
mentioned protocols |
There are three major kinds of cholesterol, High Density
Lipoprotein (HDL) , Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL),
and Very Low Density Lipoprotein (VLDL).
 |
When discussing insulin
sensitivity Robb Wolf discussed something
he called "The Deadly
Quartet". "The Deadly Quartet" consisted
of 1) Abdominal Fat 2) High Blood Glucose
3) High Triglycerides 4) High Blood Pressure
5) Inflammation.
These five factors play a huge role in insulin
sensitivity and the problems facing many
Americans today. We find the storing of abdominal
fat or
adipose fat is function of inflammation,
horomonal issues and high insulin levels.
High blood glucose
levels stem from an over-abundance of carbohydrates
that cause blood glucose levels to be high.
High triglycerides are related to extra insulin
that
can not enter the cell. High blood pressure
and Inflammation. All these factors related
to insulin
sensitivity are deadly and are related to
the consumption of carb rich meals. |
LDL Cholesterol is considered "bad
cholesterol" because cholesterol deposits form
in the arteries when LDL levels are high. An LDL level
of less than 130 is recommended, 100 is optimal, values
greater than 160 are considered high risk and should
be followed up by your physician. Those persons who
have established coronary or vascular disease may be
instructed by their doctor to get their LDL Cholesterol
well below 100. You should ask your doctor which LDL
target he or she wants for you. There are two ways
to report LDL. The most common is simply an estimate
calculated from the Total Cholesterol, HDL, and triglycerides
results. This may say "LDL Calc" . A directly
measured LDL Cholesterol is usually more accurate,
but more expensive and may require that your doctor
specify the direct LDL.
|
Here are two people. The MRI shows
one that is a healthy weight and another that is
obese. Notice anything? My observations include
1) the obese person's knees look ready to buckle
2) the obese person's heart has shifted to accomidate their girth.
3) the obese person has lots of undigested food in their system.
It looks like a whole sausage is rotting in their colon.
4) the heart on the obese MRI looks like a fatty steak. It has enlarged.
|
This Guy Definitely needs a blood
laser unit
HDL cholesterol is a ‘good cholesterol’ as
it protects against heart disease by helping remove
excess cholesterol deposited in the arteries. High
levels seem to be associated with low incidence of
coronary heart disease.
Based on the food control, TC level of
the laser group dropped 5.8% (P=0.031), and
TG dropped 8.8%. And at the same time the ALT
level of the laser group dropped 23.1% (P=0.022),
which meant that the laser therapy could protect
the liver function.
Low-intensity laser irradiation has various
bio-effect, present study showed Intra-vascular
Low lever Laser Irradiation (ILLLI) has obvious
therapeutic effects on ischemic cardiac and
cerebral vascular diseases[1,2].
Base and clinical research indicate that ILLLI
can improve hemorrheological properties, improve
blood circulation, especially microcirculation;
regulate immunity; enhance enzyme activity,
detoxify; this eliminate free radical, restrain
formation thrombus, enhance activity of enzyme
Na+-K+-ATP in red cell
membrane, raise level of SOD (this enzyme can
eliminate free radical), which helps eliminate
free radical, anti-old, improve blood hyperkinesias;
it can also increase red cell metabolic ability,
improve hemorrheological properties, decrease
blood viscosity; regulate fibro-lysis and other
bio-effects[3-5]. More |
Triglyceride is fat in the blood which,
if elevated, has been associated with heart disease,
especially if over 500 mg. High triglycerides are also
associated with pancreatitis. Triglyceride levels over
150 mg/dl may be associated with problems other than
heart disease. Ways to lower triglycerides: 1) weight
reduction, if overweight; 2) reduce animal fats in
the diet: eat more fish; 3) take certain medications
your physician can prescribe; 4) get regular aerobic
exercise; 5) decrease alcohol and sugar consumption—alcohol
and sugar are not fats, but the body can convert them
into fats then dump those fats into your blood stream
6) restrict calories - carbohydrates are converted
to triglycerides when eaten to excess.
VLDL (very low density lipoprotein) is another carrier
of fat in the blood.
"In the study published in
Alcohol, researchers from Japan’s Hyogo College of Medicine
assessed the impact of heavy drinking on a person’s
LDL cholesterol levels, HDL cholesterol levels,
triglyceride levels and overall buildup of
blood-borne fats. They conducted this assessment
with the
help of a group of middle-aged men split into
three categories: non-drinkers, occasional
heavy drinkers and regular heavy drinkers.
On the days
they drank, both the occasional heavy drinkers
and regular heavy drinkers consumed enough
alcohol to exceed moderate intake by roughly
100 percent
to 200 percent.
The researchers came to several conclusions
after comparing the cholesterol, triglyceride
and overall blood-borne fat levels of the three
participant subgroups. First, they found that
in comparison to both non-drinkers and regular
heavy drinkers, occasional heavy drinkers have
unusually high levels of triglycerides and
low levels of protective HDL cholesterol. They
also found that both occasional heavy drinkers
and regular heavy drinkers have significantly
higher levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol
and significantly lower levels of “good” HDL
cholesterol than non-drinkers"
Source |
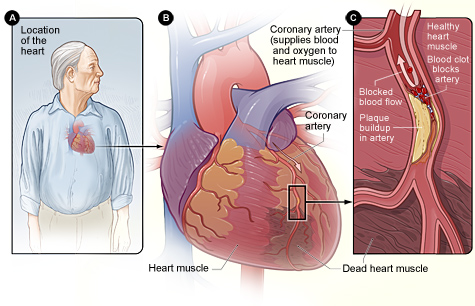
What Is Coronary Artery
Disease?
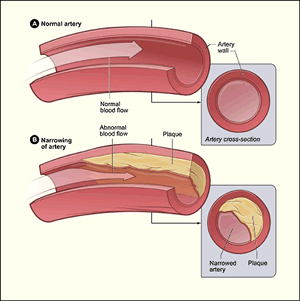
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease, is
a condition in which plaque (plak) builds up inside the coronary arteries.
These arteries supply your heart muscle with oxygen-rich blood.
Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol (ko-LES-ter-ol), calcium, and other
substances found in the blood. When plaque builds up in the arteries,
the condition is called atherosclerosis (ATH-er-o-skler-O-sis).
Plaque narrows the arteries and reduces blood flow to your heart muscle.
It also makes it more likely that blood clots will form in your arteries.
Blood clots can partially or completely block blood flow
Artery Disease Begins
in Childhood
The study examined the arteries of young people who
died of other causes, such as suicide, homicides and
accidents.
One-fifth of the young men aged 30-34 already had
advanced plaques, or deposits of fat, inside their
coronary artery, pointing the way toward future heart
attacks and strokes. Males were more than twice as
likely to have the plaques than women of the same age
range.
The biggest risk factors for a clogged artery were
found to be obesity and a high level of low-density
lipoprotein or LDL, the so-called bad cholesterol that
forms deposits on artery walls. Those with LDL levels
above 160 milligrams per deciliter were 2 ½ times
more likely to have one of these advanced plaques.
Other risk factors, such as smoking, high blood pressure,
and having a low level of high-density lipoprotein
or HDL, known as the “good” cholesterol,
also put people at a slightly higher risk of artery
blockage. Source
"First, each time new nicotine arrives
in our brain it causes the body to activate
its fight or flight stress defenses. This
in turn causes the immediate release of stored
fats into the bloodstream, fats intended
to be used to provide the instant energy
needed to either fight or flee the saber
tooth tiger. But there is no tiger
The heavy blasts of stored fats released
by nicotine stick to vessel walls damaged
by toxic
carbon monoxide. Sound bad? It gets worse.
We've recently learned that nicotine itself,
inside
our vessels, somehow causes the growth of
new blood vessels (vascularization) that
then provides
a rich supply of oxygen and nutrients to
the fats and plaques that have stuck to damaged
vessel
walls. This internal nicotine vascularization
(vessels within vessels) hardens a smoker's
arteries and veins and further accelerates
their narrowing
and clogging." |
Later
During the aging process the artery walls may become
weakened. Coronary artery disease occurs when deposits
of fatty material, cholesterol and other substances
form plaque that collects in the thinned or weakened
parts of the artery wall. The plaque may then thicken
and harden forming calcium deposits that may eventually
block the arteries and restrict blood flow to the heart.
This condition is known as atherosclerosis or "hardening
of the arteries."
A blockage in an artery also increases the pressure
of blood pumping through the vessel causing high blood
pressure. Elevated blood pressure requires the heart
to work much harder to pump blood to all body parts
in need. Over time as the heart is forced to work at
unusually high levels, it can become enlarged and lose
its' ability to function. High blood pressure is the
number one risk factor for heart disease and congestive
heart failure, a condition where the heart is no longer
able to pump enough blood to meet the demands of the
body.
Symptoms
of Coronary Artery Disease
The most common symptom of coronary artery disease is angina, or
chest pain. Angina can be described as a discomfort, heaviness, pressure,
aching, burning, fullness, squeezing, or painful feeling in your
chest. It can be mistaken for indigestion or heartburn. Angina is
usually felt in the chest, but may also be felt in the shoulders,
arms, neck, throat, jaw, or back.
Other symptoms of
coronary artery disease include:
Shortness of breath
Palpitations (irregular heart beats, skipped beats, or a "flip-flop" feeling
in your chest)
A faster heartbeat
Weakness or dizziness
Nausea
Sweating
Silent
heart attacks |
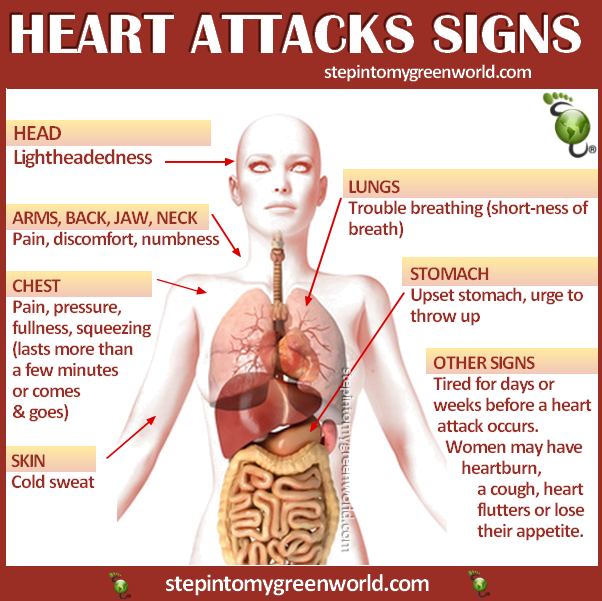
Discomfort, pressure,
heaviness, or pain in the chest,
arm, or below the breastbone
Discomfort radiating to the back, jaw, throat, or arm
Fullness, indigestion, or choking feeling (may feel like heartburn)
Sweating, nausea, vomiting, or dizziness
Extreme weakness, anxiety, or shortness of breath
Rapid or irregular heartbeats |
|
If an individual
is not treated within four to
six minutes from the onset of
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA),
the results can be fatal. An
SCA can be corrected via a shock
from an external defibrillator
or an implantable cardioverter
defibrillator (ICD).
|
Unfortunately, as the name suggests,
SCA usually occurs without any warning.
As many as 2/3’s of people
who have attacks have no prior indication
of heart disease. However, there
are some symptoms that can help you
identify if someone has just had
an SCA: sudden collapse, loss of
consciousness, abnormal breathing,
an inability to find a pulse and
loss of blood pressure. |
The most common heart attack symptom is chest
pain or discomfort. Most heart attacks involve
discomfort in the center or left side of the chest
that often lasts for more than a few minutes or
goes away and comes back.
The discomfort can feel like uncomfortable pressure,
squeezing, fullness, or pain. The feeling can be
mild or severe. Heart attack pain sometimes feels
like indigestion or heartburn.
The symptoms of angina can be similar to the symptoms
of a heart attack. Angina pain usually lasts for
only a few minutes and goes away with rest.
Chest pain or discomfort that doesn’t go
away or changes from its usual pattern (for example,
occurs more often or while you’re resting)
might be a sign of a heart attack. If you don’t
know whether your chest pain is angina or a heart
attack, call 9–1–1.
All chest pain should be checked by a doctor.
Other common signs and symptoms of a heart attack
include:
Upper body discomfort in one or both arms, the
back, neck, jaw, or upper part of the stomach
Shortness of breath, which may occur with or before chest discomfort
Nausea (feeling sick to your stomach), vomiting, light-headedness or fainting,
or breaking out in a cold sweat
Sleep problems, fatigue (tiredness), or lack of energy
Saturated fats
linked to Alzheimer's
By Wendy Zukerman for ABC Science
Posted Tue Sep 8, 2009 4:48pm AEST
The researchers found that saturated fats damage
the blood vessel lining, allowing amyloids to enter
the brain. (stock.xchg) More
According to the World Health Organisation, depression
is one of the most important diseases in the world;
15% of individuals diagnosed with severe depression
end in suicide. This is a very real problem that
stems from many places. The question I am asking
is could diet play a role in depression and suicide?
Lets take a look...
When you feel tired or down what do you do?
A Red Bull? A large cup of Starbucks? What
about a chocolate bar or a sugary snack that
instantly gives you a rush and allows you to
fight off that feeling of being down. These
give you a rush...make you feel more alert
and make you feel better and ready to continue
with your day. When you eat sugar and carbohydrates
your blood sugar rises and a rush is felt.
When you eat carbohydrates the body releases
serotonin and this effects the brain and can
alter your mood. Serotonin has been linked
to an exhausting list of conditions, including
depression, autism, eating disorders, schizophrenia,
obsessive/compulsive disorder, premenstrual
syndrome, anxiety, panic disorder, seasonal
affective disorder, extreme violence, hostility
and aggression, suicide, migraine, manic depression
and addiction. . |
CANCER
Clinical studies have found a relationship between
excess body fat and the incidence of cancer. By itself,
body fat is thought to be a storage place for carcinogens
(cancer-causing chemicals) in both men and women. In
women, excess body fat has been linked to a higher
rate of breast and uterine cancer; in men, the threat
comes from colon and prostate cancer.
Excess Body Fat Causes
Cancer
The World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF) report is the
most comprehensive ever published on the link between
cancer and diet, physical activity and weight. Searches
at nine academic institutions across the world for
studies published since records began in the 1960s
initially found half a million - 7,000 of which were
judged to be the most relevant and robust for inclusion
in the report.
It includes 10 recommendations from a panel of 21
world-renowned scientists that represent the most definitive
and authoritative advice that has ever been available
on how the general public can prevent cancer. Unicef
and the World Health Organization were among the official
observers of the report's process.
And its key finding is that maintaining a healthy
weight (a BMI of 20-25) is one of the most important
things you can do to prevent cancer. The number of
types of cancer where there is "convincing" evidence
that body fat is a cause has risen from one to six
since the last WCRF report was published in 1997, including
colorectal cancer and post-menopausal breast cancer.
Prof Sir Michael Marmot, Chair of the Panel, said: "We
are recommending that people aim to be as lean as possible
within the healthy range, and that they avoid weight
gain throughout adulthood.
"This might sound difficult, but this is what
the science is telling us more clearly than ever before.
The fact is that putting on weight can increase your
cancer risk, even if you are still within the healthy
range.
"So the best advice for cancer prevention is
to avoid weight gain, and if you are already overweight
then you should aim to lose weight."
Other findings in the report include:
There is "convincing" evidence that processed
meats, including ham and bacon, increase the risk of
colorectal cancer. People who consume them are advised
to do so sparingly.
The evidence that red meat is a cause of colorectal
cancer is stronger than ever before. People should
not eat any more than 500g of red meat a week.
This figure is for cooked meat, and is the equivalent
of between 700 and 750g of non-cooked meat.
In one of the first times a cancer report has made
a breastfeeding recommendation, mothers are advised
to breastfeed exclusively for six months and to continue
with complementary breastfeeding after that. This is
because of "convincing" evidence that breastfeeding
protects the mother against breast cancer and "probable" evidence
that it protects the child against obesity later in
life. Source
The treatment principle of the laser therapy instrument
for hyperlipemia is to irradiate the nasal cavity with
low intensity laser whose wavelength is 650nm, after
the laser energy is absorbed by the capillary vessels
in the nasal cavity, it can alter the gathering ability
of the thrombocyte and erythrocyte, improve the oxygen-carrying
capacity of the erythrocyte, restore the original negative
charge carried by the erythrocyte, increase the repulsive
force between them, separate the erythrocyte that gather
into block, improve the morphotropy and liquidity of
the erythrocyte, and thus decrease the erythrocyte
sedimentation, blood viscosity and plasma viscosity.
It can activate the various enzymes in the blood through the photochemical
action, such as the lipoprotein enzyme, transferase for lecithin and
cholesterol, acyltransferase and superoxide dismutase (SOD);, and thus
dissolve and decompound the plethoric lipid in the blood, promote the
fall of the blood fat, enhance the oxidation resistance of the body,
decrease the peroxidation of the lipid, and maintain the metabolic balance
of the fat in the body.

 NOW YOU
CAN LOWER YOUR BLOOD FATS NOW YOU
CAN LOWER YOUR BLOOD FATS
Every once in a while a technology is
introduced that transforms the landscape of health
care. Low Level Laser Therapy is a perfect example
of such a development. It is well accepted, painless
and, bottom line, it gets results.
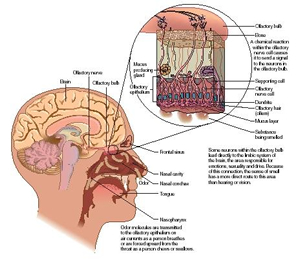
The
Blood laser system applies low-intensity laser
with the wavelength of 650nm to irradiate the nasal
cavity and inject monochromatic photons of low-intensity
into blood to increase the amount of enzymes in your
blood for dissolving the fat layers and cholesterol,
such as lipoproteinase, cholesterol transferase etc.
After the fat layer wrapping around the erythrocyte
is shucked off ,the uptake ability of the erythrocyte
is recovered and the oxygen-carrying function is
improved. Meanwhile, the negative charges on the
erythrocyte surface are recovered because the surface
layer wrapping around the erythrocyte is shucked
off, which makes the increases repuls force between
each two erythrocytes .
To
explore the effects of low-intensity laser nasal
irradiation (650nm/5mW) on dyslipedemia.

Low level laser therapy has been shown
to treat a wide range of disorders which, at first,
seem to have nothing or very little in common.
For example, LLLT can accelerate wound and burn healing, reduce pain
in different limbs all over the body, improve the condition of patients
after a stroke, help in treatment of diabetic angiopathy, and reduce
stiffness and inflammation.
The physiological effects of laser light
at low intensity are not completely understood, but
what is known is that it has three main effects:
• biostimulation/tissue regeneration biostimulation/tissue regeneration
•  anti-inflammatory anti-inflammatory
•  analgesic (pain relieving) analgesic (pain relieving)
One of the most important effects of LLLT is that
it speeds up Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production,
by increasing physical and chemical changes at the
cellular level, and enabling the cells deprived of
blood flow in the damaged tissue to heal and to attain
their normal functions.
ATP is an organic compound composed of adenine, the sugar ribose, and
three phosphate groups. It captures chemical energy obtained from the
breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes,
serving as the major energy source within the cell. Think of it as our
cell's nuclear power plants.
ATP is present in every cell, and essentially all
the physiological mechanisms that require energy for
operation obtain it directly from stored ATP.
When energy is needed by the cell, it is converted
from storage molecules into ATP. ATP then serves as
a shuttle, delivering energy to places within the cell
where energy-consuming activities are taking place.
Assistant
Treatment on Craniocerebral Injury
Outside the cell, ATP has been found to act as a neurotransmitter.
ATP receptors are widespread through the body. On its
own it is known to have effects in the arteries, intestines,
lungs, and bladder. It is also often released in tandem
with other neurotransmitters, perhaps to add chemical
stability.
Low-intensity radiation in the red and infrared spectral
ranges induces certain changes in the body,these play
an important role in achieving the clinical therapeutic
effects of this device.
The most important of these effects is improved blood micro-circulation
, which further enhances the therapeutic effect of the low-level laser
therapy device. The biological effect is due to the dilating of small
blood vessels, a decrease in the adhesive ability of blood cells, and
aiding in the formation of new micro-vessels.
In addition, low-intensity radiation has a positive
influence on the quantity and quality of the immune
system, leading to increased destruction of bacteria.
Study of the Therapy Effects of Low-Intensity
Laser Nasal Radiation on Dyslipedemia
Vital Laser + Green Therapeutics=Pure Blood!
Laser, is the “the most pure” energy that does not depend
on any materials to enters the human body.
The “low strength laser therapy" is praised as a “21st
centuries green therapy" by the international
medical science field. Laser can produce efficacy in live organize spread
of process, such as
the light effect, hot effect, the living creature stimulates effect,
strong electromagnetism effect, etc.,
and induce the answer responds of body, and no vestiges, no side effect.
Another unique
feature of Laser is that can heal pathological tissue, with no side effect
to normal tissue.
Prevent
Thrombosis
Light illuminating to blood can reduce angiotensin,
increase diastole in, decrease the content of thrombosis
material, and effectively prevent thrombus disease
of heart and brain such as cerebral stroke, cerebral
infarction, myocardial infarction and arteriosclerosis.
Lower Blood Pressure
Concentrating photons on blood can lower blood viscosity
to ameliorate the conglomeration of red blood cells
and platelets, then to decrease circumferential resistance
as a result. In addition, to lower blood fat, improve
vascular elasticity, restore hypertension, release
cardiac burden and balance blood pressure.

Ameliorate Clinical
Symptoms
Light illuminating to blood can ameliorate the symptoms
of headache, dizziness, stifle, shortness of breath,
amnesia, and fatigue caused by high blood viscidity
and high blood fat, because semiconductor laser light
can ameliorate the blood circulation, increase the
decomposing of fat - protein, decrease the peripheral
obstruction, lysis the whole body symptoms and improve
endurance.
Blocked
Arteries can cause erection problems

"If you have not had a heart attack,
incorporate lifestyle measures into your repertoire
to decrease the likelihood of you having one. If
you have suffered a heart attack, there is much that
you can do to increase your level of wellness and
improve your chances of living a long, healthy life."
Is
this ALSO a Laser version of the Bob Beck System ?

All
in one Nasal Laser
 |
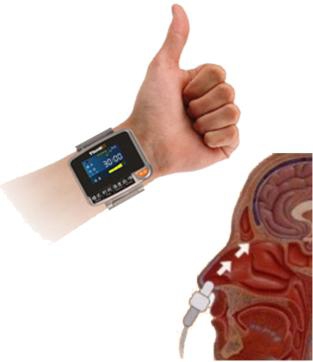
Laser Ear
Treatment
Laser
probe for nose 650nm
laser diode Max 5mW for each laser
diode
Laser
watch for wrist 650nm
laser diode Max 5mW for each laser
diode
Laser
Output 10 Wrist laser
+ 2 nasal probes + 2 Ear Probes
Time setting, 10min, 20min,
30min, 40min, 50min, 60min.
For general use, they suggested
30min Two to three times a day. (Wear only
ON left wrist)
Instruuctions
One year warranty
|
| |
|
|
|
Multi
Therapy System
Sadly The web
page authors after 25 years of working with alternative
health in our Free alternative clinic,are not allowed
to endorse the accuracy or reliability of any of
the information,
content or
guidelines
(collectively,
the "Materials") contained on, distributed
through, or linked, downloaded or accessed from these
links. You hereby acknowledge that any reliance upon
any Materials shall be at your sole risk.
|

