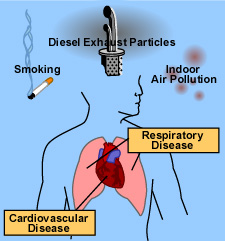
Exposure to air pollution is associated with numerous
effects on human health, including pulmonary, cardiac, vascular,
and neurological impairments. The health effects vary greatly
from person to person. High-risk groups such as the elderly,
infants, pregnant women, and sufferers from chronic heart
and lung diseases are more susceptible to air pollution.
Children are at greater risk because they are generally more
active outdoors and their lungs are still developing. Exposure
to air pollution can cause both acute (short-term) and chronic
(long-term) health effects.
The health of our lungs and entire respiratory
system is affected by the quality of the air we breathe.
In addition to oxygen, this air contains other substances
such as pollutants, which can be harmful. Exposure to chemicals
by inhalation can negatively affect our lungs and other
organs in the body. The respiratory system is particularly
sensitive to air pollutants because much of it is made
up of exposed membrane. Lungs are anatomically structured
to bring large quantities of air (on average, 400 million
litres in a lifetime) into intimate contact with the blood
system, to facilitate the delivery of oxygen.
The inhalation of air pollutants
eventually leads to their absorption into the bloodstream
and transport to the heart. A wide spectrum of
chemical and biological substances may interact
directly with the cardiovascular system to cause
structural changes, such as degenerative necrosis
and inflammatory reactions. Some pollutants may
also directly cause functional alterations that
affect the rhythmicity and contractility of the
heart. If severe enough, functional changes may
lead to lethal arrhythmias without major evidence
of structural damage to the myocardium. |
Examples of short-term effects include
irritation to the eyes, nose and throat, and upper respiratory
infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia. Other symptoms
can include headaches, nausea, and allergic reactions.
Short-term air pollution can aggravate the medical conditions
of individuals with asthma and emphysema. In the great "Smog
Disaster" in London in 1952, four thousand people
died in a few days due to the high concentrations of pollution.
| The lungs are the organs responsible for absorbing
oxygen from the air and removing carbon dioxide from
the blood-stream. Damage to the lungs from air pollution
can inhibit this process and contribute to the occurrence
of respiratory diseases such as bronchitis, emphysema,
and cancer. This can also put an additional burden
on the heart and circulatory system. |
Long-term health
effects can include chronic respiratory
disease, lung cancer, heart disease, and even damage
to the brain, nerves, liver, or kidneys. Continual
exposure to air pollution affects the lungs of growing
children and may aggravate or complicate medical conditions
in the elderly. It is estimated that half a million
people die prematurely every year in the United States
as a result of smoking cigarettes.
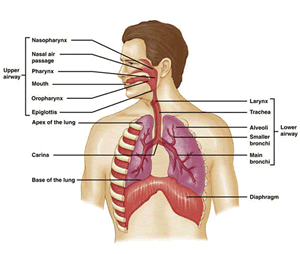
Although in humans pollutants can affect the skin,
eyes and other body systems, they affect primarily
the respiratory system. Air is breathed in through
the nose, which acts as the primary filtering system
of the body. The small hairs and the warm, humid
conditions in the nose effectively remove the larger
pollutant particles. The air then passes through
the pharynx, esophagus, and larynx before reaching
the top of the trachea. The trachea divides into
two parts, the left and the right bronchi. Each
bronchi subdivides into increasingly smaller compartments.
The smallest compartments of the bronchi are called
bronchioles, which contain millions of air sacs
called alveoli. Together, the bronchioles and alveoli
make up the lungs. |
Both gaseous and particulate air pollutants can
have negative effects on the lungs. Solid particles
can settle on the walls of the trachea, bronchi,
and bronchioles. Most of these particles are removed
from the lungs through the cleansing (sweeping) action
of "cilia", small hairlike outgrowths of
cells, located on the walls of the lungs. This is
what occurs when you cough or sneeze.
A cough or sneeze transports the particles to
the mouth. The particles are removed subsequently
from the body when they are swallowed or expelled.
However, extremely small particles may reach the
alveoli, where it takes weeks, months, or even
years for the body to remove the particles. Gaseous
air pollutants may also affect the function of
the lungs by slowing the action of the cilia. Continuous
breathing of polluted air can slow the normal cleansing
action of the lungs and result in more particles
reaching the lower portions of the lung. |

Smoke from burning forests and peat can linger
in the atmosphere for weeks, travelling thousands of miles
and harming the health of populations living far away Source
Since the start of 2020, Russia has seen an estimated
19 million hectares (73,359 square miles) consumed
by wildfires, according to Greenpeace International’s
analysis of satellite images. Nasa has warned that
abnormally warm temperatures in eastern Siberia – particularly
in the Sakha Republic, more than 1,250 miles (2,000km)
away from Krasnoyarsk – have led to more intense
and widespread fires than normal.
In the first few months of 2020, Australia grappled
with the worst wildfire season in its history. It claimed
the lives of 33 people, destroyed thousands of homes
and saw 18 million hectares (69,500 square miles) burned.
And this August, thousands of lightning strikes triggered
hundreds of fires across California, leading to a state
of emergency being declared as the flames threatened
densly populated residential areas. Beset by a prolonged
drought, the state experienced its most destructive and
deadliest fires in recorded history during 2017 and 2018.
This year California, Washington and Oregon are fighting
deadly wildfires that have burned millions of acres of
land – up to 400 hectares (1,000 acres) are burning
every 30 minutes Source |
Research into the health effects of air pollution
is ongoing. Medical conditions arising from air pollution
can be very expensive. Healthcare costs, lost productivity
in the workplace, and human welfare impacts cost billions
of dollars each year.
|
In addition to causing
lung damage, air pollution is now also recognized
as a threat to cardiovascular health. Reporting in
the March 6, 2002 Journal of the American Medical
Association (JAMA), researchers examined long-term
health data on 500,000 individuals to compare increases
in air pollution levels with incidence of death.
They discovered that when air pollution levels suddenly
increased, in addition to expected increases in deaths
from asthma, pneumonia, and emphysema, there was
an unexpected increase in the number of deaths related
to heart attacks and stroke. Most surprising was
the finding that when air pollution levels rose,
so did deaths from all causes, not just those related
to the heart and lungs (Fig. 1).
|
One possible explanation for the increase
in cardiovascular-related deaths is that air pollution
causes oxidative stress that, in turn, triggers an inflammatory
response in the lungs that leads to the release of chemicals
that impair heart function and blood pressure.
Many chemical substances may
cause the formation of reactive oxygen. This oxidative
metabolism is considered to be critical to the
preservation of cardiovascular function. For example,
oxygen free radicals oxidize low-density lipoproteins,
and this reaction is thought to be involved in
the formation of the atherosclerotic plaques. Oxidized
low-density lipoproteins can injure blood vessel
cells and increase adherence and the migration
of inflammatory cells to the injured area. The
production of oxygen free radicals in heart tissues
have been associated with arrhythmias, and heart
cell death. |
When scientists working in the Netherlands exposed rats to
high levels of particulate air pollution, following exposure,
the researchers found that plasma levels of fibrinogen were
elevated by 20 percent, which could presumably increase blood
viscosity, leading to decreased tissue blood flow. They also
measured a 400 percent jump in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha,
and a 350 percent increase in nitric oxide synthase (NOS)
in lung fluids. The researchers speculated that as particulates
lodge in lung tissues they induce an increase in the production
of nitric oxide (NO). Under normal conditions nitric oxide
is an important neurotransmitter that aids numerous signaling
pathways involved in motor learning, protein modification,
arterial dilation and immune defense. But when conditions
trigger the overproduction of NO as seen in the Netherlands
study, the result is serious damage to the endothelial cells
lining the blood vessels of the lungs.
Another mechanism implicated in air pollution-related
heart failures involves bone marrow and atherosclerotic
plaques. Researchers in Vancouver, British Columbia found
that exposure to high levels of air pollution
stimulates bone marrow to release leukocytes and platelets
that accumulate preferentially in pulmonary capillaries.
In addition to causing damage to lung tissues, the researchers
also observed that inhalation of particulate pollution
causes changes in atherosclerotic plaque lesions that make
the deposits more vulnerable to rupture.
Indoor environment, city living,
cars, exposure to electronic devices, harmful EMF’s
(electromagnetic fields) and environmental pollution
all result in increased positive ions in the body,
Manipulating the ratio of ions towards the negative.
is very wise. |
When the air you breathe in is polluted, the oxygen that
is sent throughout your body includes the toxins that polluted
the air to begin with. When you breathe in polluted air,
the toxins begin breaking down cellular structures in your
lungs and throughout your respiratory system, resulting
in chronic respiratory distress.
They postulated that exposure to particulate air
pollution induces a systemic inflammatory response that includes
the release of inflammatory mediators that stimulate bone
marrow to release leukocytes and platelets, leading to lung
inflammation and changes of atherosclerotic plaque, making
them more vulnerable to rupture.
| Table 1: Sources,
Health and Welfare Effects for Criteria Pollutants. |
| Pollutant |
Description |
Sources |
Health Effects |
Welfare Effects |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) |
Colorless, odorless gas |
Motor vehicle exhaust, indoor sources include
kerosene or wood burning stoves. |
Headaches, reduced mental alertness, heart
attack, cardiovascular diseases, impaired fetal development,
death. |
Contribute to the formation of smog. |
| Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) |
Colorless gas that dissolves in water vapor
to form acid, and interact with other gases and particles in
the air. |
Coal-fired power plants, petroleum refineries,
manufacture of sulfuric acid and smelting of ores containing
sulfur. |
Eye irritation, wheezing, chest tightness,
shortness of breath, lung damage. |
Contribute to the formation of acid rain, visibility
impairment, plant and water damage, aesthetic damage. |
| Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) |
Reddish brown, highly reactive gas. |
Motor vehicles, electric utilities, and other
industrial, commercial, and residential sources that burn fuels. |
Susceptibility to respiratory infections, irritation
of the lung and respiratory symptoms (e.g., cough, chest pain,
difficulty breathing). |
Contribute to the formation of smog, acid rain,
water quality deterioration, global warming, and visibility
impairment. |
| Ozone (O3) |
Gaseous pollutant when it is formed in the
troposphere. |
Vehicle exhaust and certain other fumes. Formed
from other air pollutants in the presence of sunlight. |
Eye and throat irritation, coughing, respiratory
tract problems, asthma, lung damage. |
Plant and ecosystem damage. |
| Lead (Pb) |
Metallic element |
Metal refineries, lead smelters, battery manufacturers,
iron and steel producers. |
Anemia, high blood pressure, brain and kidney
damage, neurological disorders, cancer, lowered IQ. |
Affects animals and plants, affects aquatic
ecosystems. |
| Particulate Matter (PM) |
Very small particles of soot, dust, or other
matter, including tiny droplets of liquids. |
Diesel engines, power plants, industries, windblown
dust, wood stoves. |
Eye irritation, asthma, bronchitis, lung damage,
cancer, heavy metal poisoning, cardiovascular effects. |
Visibility impairment, atmospheric deposition,
aesthetic damage. |
How Negative Ions Purify
the Air ?
Most all particles in the air have a positive charge or are positively
ionized, while negative ions have a negative charge. Negative ions are
drawn to these positively charged particles by magnetic attraction to
one another. When there is a high enough concentration of negative ions
in the air, they will attract to floating particles in large numbers.
This causes the particle to become too heavy to remain airborne. As a
result, the particle will drop out of the air, keeping them out of the
breathing zone and out of the respiratory system where it can trigger
breathing and health problems.
And for a whopping one in three of us who are sensitive to
their effects, negative ions can make us feel like we are walking
on air. You are one of them if you feel instantly refreshed
the moment you open a window and breathe in fresh, humid air.

"You may be one of them if you feel sleepy when you
are around an air-conditioner, but feel immediately refreshed
and invigorated when you step outside or roll down the car
window," Howard tells WebMD. "Air conditioning
depletes the atmosphere of negative ions, but an ion generator
re-releases the ions that air conditioners remove." Source |
Then the pollutant particles can be collected by normal cleaning
activities, such as dusting or vacuuming. If the particle are forced
back up into the air it will again be ionized and quickly settled
out of the breathing zone once again.
Nobel Prize in Physiology/Medicine
1991 was awarded to Dr. Neher & Sakmann for their discoveries
concerning the function of single ions channels in cells
In Brief: they discovered that all cells
open and close their cell wall 'doors' with ions. And
if they are not present, then the doors to nutrients
and the doors to waste removal are closed. If there are
not enough ions to go around, then some (or many) cells
suffer. Think garbage strike: no trucks picking up trash,
it sits in the streets and rots/smells. Source |
In nature, negative
ions are generated by processes such as sunlight, lightening,
waves from the ocean, and from waterfalls. “Concrete
Jungles” minimize the natural production of negative
ions by disrupting the delicate electrical balance between
the atmosphere and the earth. Most ionizers recreate them
with electrodes to electrically
produce negative ions. This method produces a density that
is many times higher than the negative ion level found at
Niagara Falls, the highest natural producer of negative ions
and one
of the healthiest environments in the world.
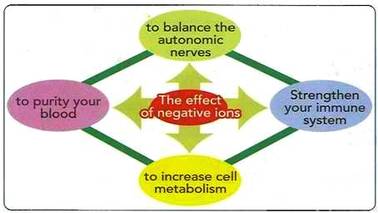
PURIFICATION OF THE BLOOD Through
research done by Dr. Tanaka in Japan, it was discovered that when
negative Ionization is introduced, the Ions in calcium and natrium
(salt) in the blood increases, and the blood is purified by increasing
blood alkaline
| In a recent study published in the Annals of the
American Thoracic Society, researchers looked at the
link between
obstructive sleep apnea and two common air pollutants — a
type of fine particle pollution known as PM2.5 and nitrogen
dioxide. Source |
NEGATIVE IONS AND SLEEP Drs.
M. Terman and J.S. Terman at Columbia University studied the effect
of negative ions on seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
They concluded that negative ions promote alpha brain waves and
increase brain wave amplitude, which translates to a higher awareness
level. Negative ion induced alpha brain waves were found to spread
evenly across the right and left brain hemispheres. All of this
creates an overall calming effect and will help us enter sleep
rapidally sp and reach the REM (rapid eye movement) state more
quickly.
REVIVING THE CELL When
the amount of negative Ions in the blood is increased, the function
of a cell is activated. The electrical material exchange speeds
up the cell function and as a result, nutrition is fully absorbed
by the cell and waste material is eliminated. Metabolism is increased
and the function of the cell is gradually revived.
NEGATIVE IONS AND DEPRESSION Columbia University studies of people
with winter and chronic depression show that negative ion generators
relieve
depression
as much as antidepressants. "The best part is that there are
relatively no side effects, but we still need to figure out appropriate
doses and which people it works best on," he says.
INCREASING IMMUNITY As
the amount of negative Ions increase, the gamma globulin in the
blood increases, resulting in blood rich in protein and antibodies.
4. ENHANCING THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS
SYSTEM Dr. Tanaka found that negative ions
control the balance in the autonomic nervous system between
the insulin and adrenal functions. This provides strong resistance
to diseases
Vitamins of the Air?
Generally speaking, negative ions increase the flow of oxygen
to the brain; resulting in higher alertness, decreased drowsiness,
and more mental energy," says
Pierce J. Howard, PhD, author of The Owners Manual for the Brain: Everyday Applications
from Mind Brain Research and director of research at the Center for Applied Cognitive
Sciences in Charlotte, N.C.
Negative Ion Air Purifiers...These devices work by generating
a flow of negative ions that charge and bind together airborne
particulate matter, which then clumps and precipitates out of the
air. Ion generating devices have been shown to be effective against
dust, cigarette smoke, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, viruses,
and bacteria. In addition to eliminating harmful particulates from
the air, negative ions also have a number of unique health benefits.
Plus UV-C light, When properly utilized,
this invisible form of light can safely kill germs, mold,
mildew, and in some cases even bacteria and viruses.
With an air purifier with UV-light technology, air is pulled
into the appliance and passes through a fine filter, such
as a HEPA filter. The air then passes through a small internal
chamber where it is exposed to UV light. The UV-C light is
not released into the room, so you won’t see it nor
will you be exposed to it.
Our
Latest heavy
Duty 5 in1 Delux Home Tower
Air purifier
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

UV Purple Light Germicidal Disinfection

Negative Ion Generator
Five Air Purification protocols in one unit
|
Our
Latest heavy
Duty 5 in1 Delux Home Tower
Air purifier
Air Purifier UV Sterilize Negative Ion
generator Remove Smog Dust PM2.5 , Air bornes bacteria
and virus
Applicable Area:
20-40 m2
Key Features
Efficient eliminate airborne contaminates such as dust, pollen, mold, smoke,
pet dander, and bacteria, germs, allergens.
UV lamp destroys micro-organisms such as germs, viruses
and bacteria, and helps create a healthier environment.
Quiet operation.
Runs 7-24 cleaning.
low energy use
Particulate CADR 200m3/H
HEPA Filter Negative Ions Anion Ionization Air Purifier
UV Light
Filter:
Pre-filter + HEPA + Activated Carbon
Sensor:
Dust Sensor/PM2.5 Sensor
Negative Ion:
8 million
UV Sterilize
Voltage 120-240V
|

 |
Filter Replacement Pack
|
| |
|
 |
UV sterilizer Replacement tube
|
|
| |
|
|
Are you Getting Enough Oxygen ?
Oxygen is one of the most important keys to good health,
but not everyone is aware of it. Currently scientists are
examining the role oxygen starvation plays in the development
of disease.
CE Approved Black only
Accurate oxygen saturation and pulse rate data in seconds
Easy to use; automatically turns on/off with finger insertion/removal
Compact size fits easily into a pocket
|
| |
|
|

