|
"Scientists are not absolutely sure what causes Alzheimer’s
but plaques and tangles are prime suspects in cell death
and tissue loss in the Alzheimer brain.
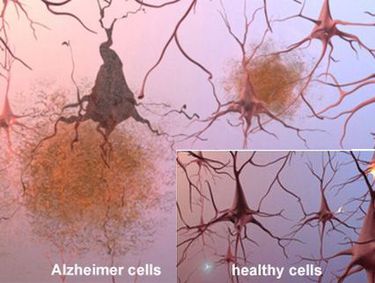
Plaques are abnormal clusters of chemically “sticky” proteins
called beta-amyloid that build up between nerve cells.
The most damaging form of beta-amyloid may be groups of
a few pieces rather than the plaques themselves. The small
clumps may block cell-to-cell signaling at synapses. They
may also activate immune system cells that trigger inflammation
and devour disabled cells." Source
"Tangles form inside dying cells. Tangles are twisted
fibers of a protein called tau. In healthy areas, tau
helps keep the transport system on track. But in areas
where tangles are forming, the twisted strands of tau
essentially disintegrate the transport system so that
nutrients and other essential supplies can no longer
move through the cells, which eventually die" |
"A combination of high blood pressure and decreased blood
flow inside the brain may spur the buildup of harmful plaque
and signal the onset of dementia, USC researchers have
found.
“If you have problems with the blood vessels in
the brain, then you’re going to end up with difficulty
with thinking skills, cognition, memory, and ultimately
this can be related to other brain pathologies such as
Alzheimer’s disease,” said Daniel Nation, lead
author of the study and an assistant professor of psychology
at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.
For the study published June 1 in the journal Brain, Nation
used patient data from a national medical database, the
Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative housed
at the Keck School of Medicine at USC, to explore whether
constricted blood flow contributes to the buildup of amyloid
plaque , consequently, to the onset of dementia. He
also determined a new way to calculate cerebrovascular
resistance — a stiffening of the vessels that results
from high blood pressure and low blood flow. Source
.Neuroscientists
are getting excited about non-invasive procedures to
tune the brain’s
natural oscillations.
"In March 2015, Li-Huei Tsai set up a tiny disco for some
of the mice in her laboratory. For an hour each day, she
placed them in a box lit only by a flickering strobe. The
mice — which had been engineered to produce plaques
of the peptide amyloid-ß in the brain, a hallmark
of Alzheimer’s disease — crawled about curiously.
When Tsai later dissected them, those that had been to
the mini dance parties had significantly lower levels of
plaque than mice that had spent the same time in the dark1.
Tsai, a neuroscientist at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
(MIT) in Cambridge, says she checked the result; then checked
it again. “For the longest time, I didn’t believe
it,” she says. Her team had managed to clear amyloid
from part of the brain with a flickering light. The strobe
was tuned to 40 hertz and was designed to manipulate the
rodents’ brainwaves, triggering a host of biological
effects that eliminated the plaque-forming proteins." Source
Download Podcast
"So I have been trying the sound therapy
on my wife who is in the advanced stages of Alzheimer’s
and to my surprise after 8 days she started to
show small signs of being more mentally alert than
before. So I have continued to use your tone generator
using a 40Hz sine wave for about an hour each day.
(I’ve recently started to do it twice a day
for slightly shorter sessions).
So now 7 weeks on the improvement in her awareness
has continued to the point where she is starting
to be able to put a few words together and to
respond to questions neither of which she has
been able to do for nearly a year. "
Tomasz P. Szynalski Apr 24, 2018 |
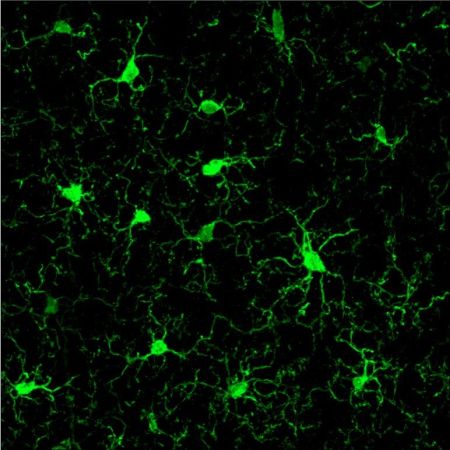
| "Those neon green things in the image
are microglia, the brain’s immune cells, or,
as we describe them in our episode, the janitor cells
of the brain.
Straight from MIT’s research files, this image
shows microglia who have gotten light stimulation therapy
(one can only hope in the flicker room). You can see
their many, super-long tentacles, which would be used
to feel out anything that didn’t belong in the
brain. And then they’d eat it!" Source |
|
Bringing Gamma Back
Podcast
"Today, a startling new discovery: prodding
the brain with light, a group of scientists got an unexpected
surprise -- they were able to turn back on a part of the
brain that had been shut down by Alzheimer’s disease.
This new science is not a cure, and is far from a treatment,
but it’s a finding so … simple, you won’t
be able to shake it. Come join us for a lab visit, where
we’ll meet some mice, stare at some light, and come
face-to-face with the mystery of memory. We can promise
you: by the end, you’ll never think the same way
about Christmas lights again." Source
"She has been using the
sound therapy for several months now, usually for
1-2 hours per day. Within about a week, we saw
some subject improvements. The improvements aren’t
major but it seems to me that her improvements
have plateaued. Even that is positive if it is
helping to prevent decline.
I have been following these scientific
development 40 Hz therapy for afew of years.
My wife has Posterior Cortical Atrophy (PCA)
which is also known a Visual Variant Alzheimer’s. "
Stockett Apr 24, 2018 |

“The implications are significant,” says
Michal Schwartz of the Weizmann Institute of Science, who
was not involved in the work. And, she says, if the effects
of gamma waves also improve cognition in Alzheimer’s
models, “it’s unbelievable.”
"Now, a growing body of evidence, including
Tsai’s findings, hint at a meaningful connection
to neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s
and Parkinson’s diseases. The work offers
the possibility of forestalling or even reversing
the damage caused by such conditions without using
a drug. More than two dozen clinical trials are
aiming to modulate brainwaves in some way — some
with flickering lights or sound, but most
through the direct application of electrical currents
to the brain or scalp (CES). They aim
to treat everything from insomnia to schizophrenia
and premenstrual dysphoric disorder."
Nature 555, 20-22 (2018) |
The science
It has been known since at least the 1980s that cognitive
activity triggers brainwaves (wave-like patterns of activation)
at a frequency of 40 Hz in humans and other mammals.
"Gamma brain waves are the
fastest brainwave frequency with the smallest amplitude.
They are associated with the “feeling of blessings” reported
by experienced meditators such as monks and nuns,
and with peak concentration and extremely high levels
of cognitive functioning.
Neuroscientists believe that gamma waves are
able to link information from all parts of the
brain
and not only that, but the entire brain is influenced
by the gamma wave."
|
"Most People have
gamma brainwave activity, but the amount of gamma waves
produced varies. Low amounts of gamma brainwave activity
have been linked to learning difficulties, poor memory
and impaired mental processing."
In 1991, researchers from
the NYU Medical Center discovered that Alzheimer’s
patients have reduced 40 Hz brainwaves compared with healthy people. (paywalled
paper)
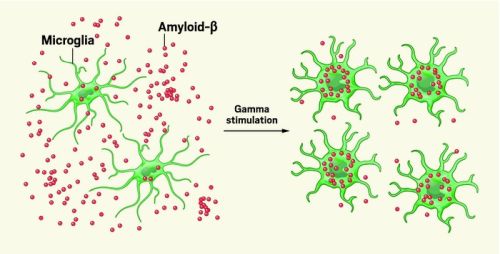
“More and more we’re finding that microglia
drive the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s and
other neurodegenerative disorders,” says Terrence
Town of the University of Southern California," |

"In 2016, MIT’s Alzheimer’s group did
experiments on transgenic mice with early Alzheimer’s
disease and found that exposing them to a light flickering
at a
frequency of 40 Hz (40 times a second) for 1 hour a day
for 7 days causes an almost 60% reduction in ß-amyloid plaques, which
are a molecular hallmark of Alzheimer’s. 20 Hz and 80 Hz tones did
not have the same effect. An important qualification here is that the effect
was
limited to the visual cortex, which is not significantly affected in human
Alzheimer’s patients. Here’s an accessibly written report in
The Atlantic and here’s the original paper (published in Nature)
if you’re
strong in science-speak. MIT also made a video about the findings."
“You can imagine these networks ping-ponging
back and forth, which allows them to generate these
gamma rhythms,” said Edward S. Boyden Boyden
is part of the MIT team and previously helped develop
the light-activated
neuron technique, also known as optogenetics." |
"According to the New Scientist (paywalled article), the
same MIT team achieved even better results by playing mice
a 40 Hz sound. ß-amyloid plaques
shrank by about 50% in the auditory cortex and – crucially – in
the hippocampus, perhaps because the two areas are close to each other.
This is a very important discovery, because the hippocampus is the region
of the
brain which is involved in forming memories. It is the hippocampus that
suffers the most damage in human Alzheimer’s patients. As of 1
Mar 2018, these results have not been published, but were presented at
the Society
for Neuroscience
conference in Washington in November 2017."

"By restoring gamma waves disrupted
by the neurodegenerative disease, “we can activate immune genes in the
brain, which kick-start microglia to remove Aß plaques
and possibly halt the progression of Alzheimer’s
disease,” said Annabelle C. Singer, a member
of the team now at Georgia Institute of Technology." |
In March 2016, scientists at the University of Toronto
published the results of a small, placebo-controlled pilot
study (paywalled paper),
in which
they exposed 20 Alzheimer’s patients to a 40 Hz sound. After six 30-minute
sessions (done twice a week), the patients’ average score on the 30-point
SLUMS scale improved by 4 points, while the placebo group did not improve.
It should be noted that the “dosage” of the treatment was rather
low, which may explain the modest results.
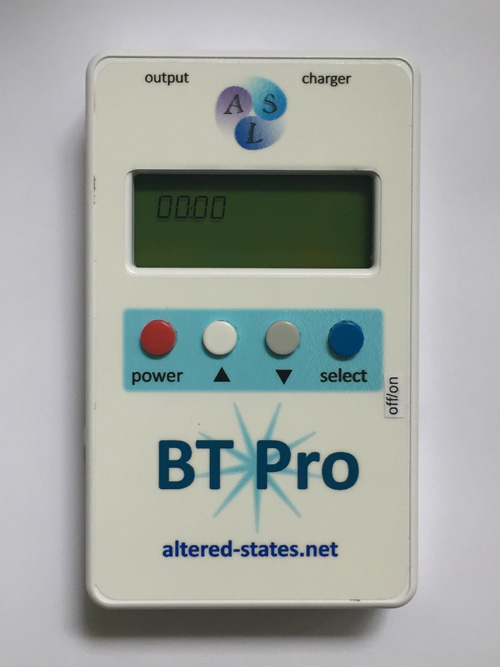
 |
BTPro with the Mind wave option
Gamma 40 hz 50hz 60 hz 70 hz 80 hz
Beta 14 hz 18hz 20hz 22hz 27hz 28hz 30hz
Alpha 9 hz 10 hz 11 hz 12 hz 13 hz
Theta 4 nz 4.5 hz 5 hz 6 hz 7 hz 7.83 hz 8.0hz
Delta 0.5hz 1 hz 2 hz 3 hz 3.9 hz
Includes earclips for CES functions
plus more built in frequencies and options here
|
| |
|
 |
Audio
Option Anti Radiation Earphones
NZ$19.54
|
| |
|
 |
Rife Pro option 0-3a
Access all The Gamma frequencies
More information here
Starting at
|
| |
|
|

