Below is a technical explanation of why alkaline, ionized
water is a lot more effective that other types of water in helping
maintain or restore wellness. It is an excellent article but probably
requires some prior understanding of basic biochemistry.
Why
Drink Alkaline Ionized Water? - The Basics
Water, The chemistry of life.
Whenever we attempt to determine whether there is life as we know
it on Mars or other planets, scientists first seek to establish whether
or not water is present. Why? Because life on earth totally depends
on water.
A High percentage of living things, both plant and animal are found
in water. All life on earth is thought to have arisen from water.
The bodies of all living organisms are composed largely of water.
About 70 to 90 percent of all organic matter is water.
The chemical reactions in all plants and animals that
support life take place in a water medium. Water
not only provides the medium to make these life sustaining reactions
possible, but water itself is often an important reactant or product
of these reactions. In short, the chemistry of life is water chemistry.
Water
not only provides the medium to make these life sustaining reactions
possible, but water itself is often an important reactant or product
of these reactions. In short, the chemistry of life is water chemistry.
Water, the universal solvent
Water is a universal, superb solvent due to the marked polarity
of the water molecule and its tendency to form hydrogen bonds with
other molecules. One water molecule, expressed with the chemical
symbol H2O, consists of 2 hydrogen atoms and
1 oxygen atom.
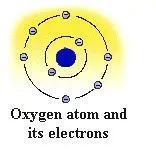 Standing
alone, the hydrogen atom contains one positive proton at its core
with one negative electron revolving around it in a three-dimensional
shell. Oxygen, on the other hand, contains 8 protons in its nucleus
with 8 electrons revolving around it. This is often shown in chemical
notation as the letter O surrounded by eight dots representing 4
sets of paired electrons.
Standing
alone, the hydrogen atom contains one positive proton at its core
with one negative electron revolving around it in a three-dimensional
shell. Oxygen, on the other hand, contains 8 protons in its nucleus
with 8 electrons revolving around it. This is often shown in chemical
notation as the letter O surrounded by eight dots representing 4
sets of paired electrons.
The single hydrogen electron and the 8 electrons of oxygen are the
key to the chemistry of life because this is where hydrogen and oxygen
atoms combine to form a water molecule, or split to form ions.
Hydrogen tends to ionize by losing its single electron and form
single H+ ions, which are simply isolated protons since the hydrogen
atom contains no neutrons. A hydrogen bond occurs when the electron
of a single hydrogen atom is shared with another electronegative
atom such as oxygen that lacks an electron.
Polarity of water molecules
In a water molecule, two hydrogen atoms are covalently bonded to
the oxygen atom. But because the oxygen atom is larger than the hydrogen's,
its attraction for the hydrogen's electrons is correspondingly greater
so the electrons are drawn closer into the shell of the larger oxygen
atom and away from the hydrogen shells. This means that although
the water molecule as a whole is stable, the greater mass of the
oxygen nucleus tends to draw in all the electrons in the molecule
including the shared hydrogen electrons giving the oxygen portion
of the molecule a slight electronegative charge.
 The
shells of the hydrogen atoms, because their electrons are closer
to the oxygen, take on a small electropositive charge. This means
water molecules have a tendency to form weak bonds with water molecules
because the oxygen end of the molecule is negative and the hydrogen
ends are positive.
The
shells of the hydrogen atoms, because their electrons are closer
to the oxygen, take on a small electropositive charge. This means
water molecules have a tendency to form weak bonds with water molecules
because the oxygen end of the molecule is negative and the hydrogen
ends are positive.
A hydrogen atom, while remaining covalently bonded to the oxygen
of its own molecule, can form a weak bond with the oxygen of another
molecule. Similarly, the oxygen end of a molecule can form a weak
attachment with the hydrogen ends of other molecules. Because water
molecules have this polarity, water is a continuous chemical entity.
These weak bonds play a crucial role in stabilizing the shape of
many of the large molecules found in living matter. Because these
bonds are weak, they are readily broken and re-formed during normal
physiological reactions. The disassembly and re-arrangement of such
weak bonds is in essence the chemistry of life.
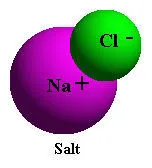 To
illustrate water's ability to break down other substances, consider
the simple example of putting a small amount of table salt in a glass
of tap water. With dry salt (NaCl) the attraction between the electropositive
sodium (Na+) and electronegative chlorine (Cl-) atoms of salt is
very strong until it is placed in water. After salt is placed in
water, the attraction of the electronegative oxygen of the water
molecule for the positively charged sodium ions, and the similar
attraction of the electropositive hydrogen ends of the water molecule
for the negatively charged chloride ions, are greater than the mutual
attraction between the outnumbered Na+ and Cl- ions. In water the
ionic bonds of the sodium chloride molecule are broken easily because
of the competitive action of the numerous water molecules.
To
illustrate water's ability to break down other substances, consider
the simple example of putting a small amount of table salt in a glass
of tap water. With dry salt (NaCl) the attraction between the electropositive
sodium (Na+) and electronegative chlorine (Cl-) atoms of salt is
very strong until it is placed in water. After salt is placed in
water, the attraction of the electronegative oxygen of the water
molecule for the positively charged sodium ions, and the similar
attraction of the electropositive hydrogen ends of the water molecule
for the negatively charged chloride ions, are greater than the mutual
attraction between the outnumbered Na+ and Cl- ions. In water the
ionic bonds of the sodium chloride molecule are broken easily because
of the competitive action of the numerous water molecules.
As we can see from this simple example, even the delicate configuration
of individual water molecules enables them to break relatively stronger
bonds by converging on them. This is why we call water the universal
solvent. It is a natural solution that breaks the bonds of larger,
more complex molecules. This is the chemistry of life on earth, in
water and on land.
Oxidation-reduction reactions
Basically, reduction means the addition of an electron (e-), and
its converse, oxidation means the removal of an electron. The addition
of an electron, reduction, stores energy in the reduced compound.
The removal of an electron, oxidation, liberates energy from the
oxidized compound. Whenever one substance is reduced, another is
oxidized.
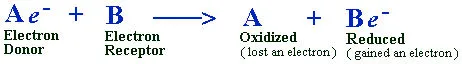
To clarify these terms, consider any two molecules, A and B, for example.
When molecules A and B come into contact, here is what happens:
B grabs an electron from molecule A.
Molecule A has been oxidized because it has lost an electron.
The net charge of B has been reduced because it has gained a negative
electron (e-).
In biological systems, removal or addition of an electron constitutes
the most frequent mechanism of oxidation-reduction reactions. These
oxidation-reduction reactions are frequently called redox reactions.
Acids and Bases
An acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen
ions (H+) in water. A base is a substance that decreases the concentration
of hydrogen ions, in other words, increasing the concentration of
hydroxide ions OH-.
The degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution is measured in
terms of a value known as pH, which is the negative logarithm of
the concentration of hydrogen ions:
pH = 1/log[H+] = -log[H+]
What is pH?
On the pH scale, which ranges from 0 on the acidic end to 14 on
the alkaline end, a solution is neutral if its pH is 7. At pH 7,
water contains equal concentrations of H+ and OH- ions. Substances
with a pH less than 7 are acidic because they contain a higher concentration
of H+ ions. Substances with a pH higher than 7 are alkaline because
they contain a higher concentration of OH- than H+. The pH scale
is a log scale so a change of one pH unit means a tenfold change
in the concentration of hydrogen ions.
Importance of balancing pH
Living things are extremely sensitive to pH and function best (with
certain exceptions, such as certain portions of the digestive tract)
when solutions are nearly neutral. Most interior living matter (excluding
the cell nucleus) has a pH of about 6.8.
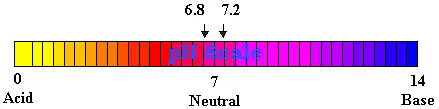
Blood plasma and other fluids that surround the cells in the body have
a pH of 7.2 to 7.3. Numerous special mechanisms aid in stabilizing
these fluids so that cells will not be subject to appreciable fluctuations
in pH. Substances which serve as mechanisms to stabilize pH are called
buffers. Buffers have the capacity to bond ions and remove them from
solution whenever their concentration begins to rise.
Conversely, buffers can release ions whenever their concentration begins to
fall. Buffers thus help to minimize the fluctuations in pH. This is an important
function because many biochemical reactions normally occurring in living organisms
either release or use up ions.
NOTE: Dr. Hayashi is a Heart Specialist and Director of the Water Institute
of Japan.
Oxygen: Too much of a good thing.
Oxygen is essential to survival. It is relatively stable in the air, but
when too much is absorbed into the body it can become active and unstable
and has a tendency to attach itself to any biological molecule, including
molecules of healthy cells. The chemical activity of these free radicals
is due to one or more pairs of unpaired electrons.
About 2% of the oxygen we normally breathe becomes active oxygen, and this
amount increases to approximately 20% with aerobic exercise.
 Such
free radicals with unpaired electrons are unstable and have a high oxidation
potential, which means they are capable of stealing electrons from other
cells. This chemical mechanism is very useful in disinfectants such as hydrogen
peroxide and ozone which can be used to sterilize wounds or medical instruments.
Inside the body these free radicals are of great benefit due to their ability
to attack and eliminate bacteria, viruses and other waste products.
Such
free radicals with unpaired electrons are unstable and have a high oxidation
potential, which means they are capable of stealing electrons from other
cells. This chemical mechanism is very useful in disinfectants such as hydrogen
peroxide and ozone which can be used to sterilize wounds or medical instruments.
Inside the body these free radicals are of great benefit due to their ability
to attack and eliminate bacteria, viruses and other waste products.
Active Oxygen in the body
Problems arise, however, when too many of these free radicals are turned
loose in the body where they can also damage normal tissue.
Putrefaction sets in when microbes in the air invade the proteins, peptides,
and amino acids of eggs, fish and meat. The result is an array of unpleasant
substances such as:
Hydrogen sulfide
Ammonia
Histamines
Indoles
Phenols
Scatoles
These substances are also produced naturally in the digestive tract when
we digest food, resulting in the unpleasant odor evidenced in feces. Putrefaction
of spoiled food is caused by microbes in the air; this natural process is
duplicated in the digestive tract by intestinal microbes. All these waste
products of digestion are pathogenic, that is, they can cause disease in
the body.
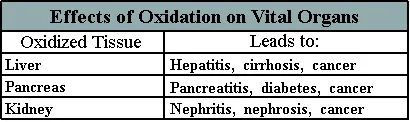
Hydrogen sulfide and ammonia are tissue toxins that can damage the liver.
Histamines contribute to allergic disorders such as atopic dermatitis, urticaria
(hives) and asthma. Indoles and phenols are considered carcinogenic. Because
waste products such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, histamines, phenols and
indoles are toxic, the body's defense mechanisms try to eliminate them by
releasing neutrophils (a type of leukocyte, or white corpuscle). These neutrophils
produce active oxygen, oddball oxygen molecules that are capable of scavenging
disintegrating tissues by gathering electrons from the molecules of toxic
cells.
Problems arise, however, when too many of these active oxygen molecules,
or free radicals, are produced in the body. They are extremely reactive and
can also attach themselves to normal, healthy cells and damage them genetically.
These active oxygen radicals steal electrons from normal, healthy biological
molecules. This electron theft by active oxygen oxidizes tissue and can cause
disease.
Because active oxygen can damage normal tissue, it is essential to scavenge
this active oxygen from the body before it can cause disintegration of healthy
tissue. If we can find an effective method to block the oxidation of healthy
tissue by active oxygen, then we can attempt to prevent disease.







Antioxidants block dangerous oxidation
One way to protect healthy tissue from the ravages of oxidation caused by
active oxygen is to provide free electrons to active oxygen radicals, thus
neutralizing their high oxidation potential and preventing them from reacting
with healthy tissue.
Research on the link between diet and cancer is far from complete, but some
evidence indicates that what we eat may affect our susceptibility to cancer.
Some foods seem to help defend against cancer, others appear to promote it.
Much of the damage caused by carcinogenic substances in food may come about
because of an oxidation reaction in the cell. In this process, an oddball
oxygen molecule may damage the genetic code of the cell. Some researchers
believe that substances that prevent oxidation -- called ANTIOXIDANTS --
can block the damage. This leads naturally to the theory that the intake
of natural antioxidants could be an important aspect of the body's defense
against cancer. Substances that some believe inhibit cancer include vitamin
C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, selenium, and gluthione (an amino acid). These
substances are reducing agents. They supply electrons to free radicals and
block the interaction of the free radical with normal tissue.
How we can avoid illness
As we mentioned earlier, the presence of toxic waste products such as hydrogen
sulfide, ammonia, histamines, indoles, phenols and scatoles impart an offensive
odor to human feces. In the medical profession, it is well known that patients
suffering from hepatitis and cirrhosis pass particularly odoriferous stools.
Excessively offensive stools caused by the presence of toxins are indicators
of certain diseases, and the body responds to the presence of these toxins
by producing neutrophil leukocytes to release active oxygen in an attempt
to neutralize the damage to organs that can be caused by such waste products.
But when an excess amount of such active oxygen is produced, it can damage
healthy cells as well as neutralize toxins. This leads us to the conclusion
that we can minimize the harmful effect of these active oxygen radicals by
reducing them with an ample supply of electrons.
Water, the natural solution
There is no substitute for a healthy balanced diet, especially rich in antioxidant
materials such as vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, and other foods that
are good for us. However, these substances are not the best source of free
electrons that can block the oxidation of healthy tissue by active oxygen.
Water treated by electrolysis to increase its reduction potential is the
best solution to the problem of providing a safe source of free electrons
to block the oxidation of normal tissue by free oxygen radicals. We believe
that reduced water, water with an excess of free electrons to donate to active
oxygen, is the best solution because:
The reduction potential of water can be dramatically increased over other antioxidants
in food or vitamin supplements.
The molecule weight of reduced water is low, making it fast acting and able
to reach all tissues of the body in a very short time.
What is IONIZED WATER?
Ionized water is the product of mild electrolysis which takes place in the
ionized water unit. The production of ionized water, its properties, and
how it works in the human body are described in the next section. Ionized
water is treated tap water that has not only been filtered, but has also
been reformed in that it provides reduced water with a large mass of electrons
that can be donated to active oxygen in the body to block the oxidation of
normal cells.
Tap water: What it is and isn't
Normal tap water, for example, with a pH of 7 is approximately neutral on
the pH scale of 0 to 14. When measured with an ORP (oxidation potential)
meter its redox potential is approximately +400 to +500 mV. Because it has
a positive redox potential, it is apt to acquire electrons and oxidize other
molecules. Reduced Ionized Water, on the other hand, has a negative redox
potential of approximately -250 to -350 mV. This means it has a large mass
of electrons ready to donate to electron-thieving active oxygen.
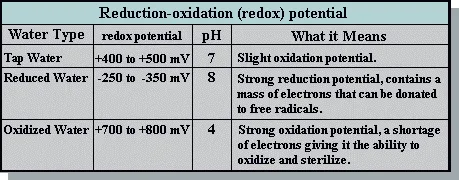
Redox potential, not pH, is the crucial factor
Traditionally we have judged the properties of water from the standpoint
of pH, in other words whether water is acidic or alkaline. According to Dr.
Yoshiaki Matsuo PhD., the inventor of the Ionized Water unit, "In my opinion,
redox potential is more important than pH. The importance of pH is over emphasized.
For example, the average pH of blood is 7.4 and acidosis or alkalosis are
defined according to deviation within the range of 7.4 +- 0.005. But nothing
has been discussed about ORP, or oxidation-reduction potential."
The pH of tap water is about pH 7, or neutral. When tap water is electrolyzed
into Ionized Water, its reduced water has a pH of about 9 and the oxidized
water a pH of about 4. Even if you make alkaline water of pH 9 by adding
sodium hydroxide or make acidic water of pH 3 by adding hydrogen chloride,
you will find very little change in the ORP values of the two waters. On
the other hand, when you divide tap water with electrolysis you can see the
ORP fluctuate by as much as +- 1,000 mV. By electrolysis we can obtain reduced
water with negative potential that is good for the body.
USING IONIZED WATER
What IONIZED WATER Does
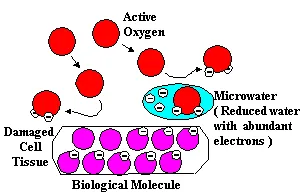
The Ionized Water unit produces two kinds of water with different redox potentials,
one with a high reduction potential and the other with a high oxidation potential.
Reduced Water
When taken internally, the reduced Ionized Water with its redox potential
of -250 to -350 mV readily donates its electrons to oddball oxygen radicals
and blocks the interaction of the active oxygen with normal molecules.
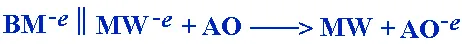
A biological molecule (BM) remains intact and undamaged.
Undamaged biological molecules are less susceptible to infection and disease.
Ionized Water gives up an extra electron and reduces the active oxygen (AO),
thus rendering it harmless. The AO is reduced without damaging surrounding
biological molecules. Substances which have the ability to counteract active
oxygen by supplying electrons are called scavengers. Reduced water, therefore,
can be called scavenging water.
When taken internally, the effects of reduced water are immediate. Ionized
Water inhibits excessive fermentation in the digestive tract by reducing
indirectly metabolites such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, histamines, indoles,
phenols and scatoles, resulting in a cleaner stool within days after reduced
water is taken on a regular basis. In 1965, the Ministry of Welfare of
Japan announced that reduced water obtained from electrolysis can prevent
abnormal fermentation of intestinal microbes.
Oxidized Water
Oxidized water with its redox potential of +700 to +800 mV is an oxidizing
agent that can withdraw electrons from bacteria and kill them. The oxidized
water from the Ionized Water unit can be used to clean hands, kitchen utensils,
fresh vegetables and fruits, and to sterilize cutting boards and minor wounds.
Tests have shown that oxidized water can be used effectively to treat athlete's
foot, minor burns, insect bites, scratches, and so on.
Dr. Yoshiaki Matsuo, Vice Director of the Water Institute of Japan, has
developed another apparatus capable of producing hyperoxidized water with
a redox potential of +1,050 mV or more, and a pH lower than 2.7. Tests have
shown that this hyper oxidized water can quickly destroy MRSA (Methecillin
Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus).
Although hyperoxidized water is a powerful sterilizing agent, it won't harm
the skin. In fact, it can be used to heal. Hyperoxidized water has proven
effective in Japanese hospitals in the treatment of bedsores and operative
wounds with complicated infections.
But perhaps the most exciting future application of hyperoxidized water
is in the field of agriculture where it has been used effectively on plants
to kill fungi and other plant diseases. Hyperoxidized water is non-toxic,
so agricultural workers can apply it without wearing special protective equipment
because there is no danger of skin or respiratory damage. An added benefit
of using hyperoxidized water to spray plants is that there is no danger to
the environment caused by the accumulation of toxic chemicals in the ground.
Ionized Water superior to antioxidant diet
Today we read much about correct dieting principles and paying attention
to what we eat in order to stay healthy. This is a sensible practice, but
it is surprising that many of us don't realize that the bulk of what eat
is composed of water. Vegetables and fruits are 90% water; fish and meat
are about 70% water as well.
Even advocates of the importance of vitamin C in diet staples have to admit
that its potency, namely, the redox potential of this important vitamin,
rapidly diminishes with age and preparation for the dining table. Carbohydrates,
the main consistent of vegetables and fruit, have a molecular weight of 180
whereas water has a much lower molecular weight of 18.
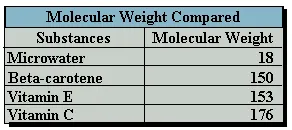
Ionized Water, with its low molecular weight and high reduction potential,
makes it a superior scavenging agent of active oxygen. But electrolysis inside
the Ionized Water unit not only charges the reduced water with electrons,
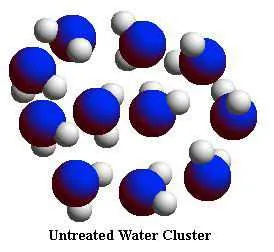
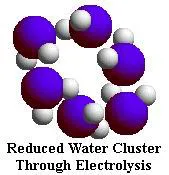
it also reduces the size of reduced water molecule clusters.
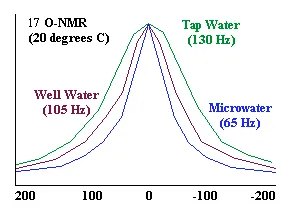 NMR
(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) analysis reveals that tap water and well water
consists of clusters of 10 to 13 2 0 molecules. Electrolysis
of water in the Ionized Water unit reduces these clusters to about half their
normal size -- 5 to 6 water molecules per cluster.
NMR
(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) analysis reveals that tap water and well water
consists of clusters of 10 to 13 2 0 molecules. Electrolysis
of water in the Ionized Water unit reduces these clusters to about half their
normal size -- 5 to 6 water molecules per cluster.
As the graph shows, the NMR signal that measures cluster size by line width
at half-amplitude shows 65 Hz for reduced water and 133 Hz for tap water,
revealing that the reduced water clusters are approximately half the size
of tap water clusters.
This is why Ionized Water is more readily absorbed by the body than untreated
tap water. Ionized Water quickly permeates the body and blocks the oxidation
of biological molecules by donating its abundant electrons to active oxygen,
enabling biological molecules to replace themselves naturally without damage
caused by oxidation that can cause diseases.
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
Upstream and downstream theory
Prevent disease at the source
According to Dr. Hidemitsu Hayashi, Director of the Water Institute of Japan, "To
eliminate the pollutants in a large stream that is contaminated at its source,
we must work on the problems upstream at the headwaters -- the source of
the pollution -- not downstream where we can only try to treat the evidence
of damage caused by the pollution. Ionized Water's contribution to preventive
medicine is essentially upstream treatment."
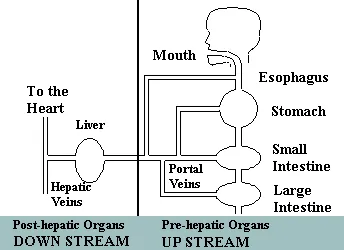
Upstream
According to our model, we consider the digestive tract upstream where we
intake water and food. Although many people today in developed countries
are growing more skeptical about what they eat, they tend to concentrate
more on what the food contains rather than the metabolized products of foods
in the digestive tract.
Upstream



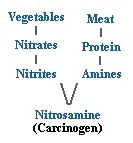 For
example, consider the typical balanced diet of meat and vegetables. Meat
protein is metabolized into amines while nitrates from fertilizers used to
grow vegetables metabolize into nitrites in the digestive tract. These amines
and nitrites combine to form nitrosamine, a recognized carcinogen.
For
example, consider the typical balanced diet of meat and vegetables. Meat
protein is metabolized into amines while nitrates from fertilizers used to
grow vegetables metabolize into nitrites in the digestive tract. These amines
and nitrites combine to form nitrosamine, a recognized carcinogen.
We've already discussed that odoriferous feces are evidence of excessive
fermentation in the digestive tract, so reduced water performs a very important
function upstream in the digestive tract by reducing this excessive fermentation
as evidenced by cleaner stools within days of starting a steady regimen of
reduced water.
Downstream



Downstream
Downstream from the digestive tract, starting at the liver, reduced water
quickly enters the liver and other organs due to, first, its lower molecular
weight, and, secondly, the size of its clusters. At tissue sites throughout
the body, reduced water with its safe, yet potent reduction potential readily
donates its passenger electrons freely to active oxygen and neutralizes them
so they cannot damage the molecules of healthy cells. Normal cells are protected
from the electron thievery of active oxygen and allowed to grow, mature,
function and regenerate without interference from rogue, oddball oxygen radicals
which tend to steal the electrons from the molecules of normal, healthy biological
molecules.
The water boom
We are now in the midst of a water boom. In Japan and other countries consumers
are buying various kinds of bottled and canned water even though water is
one of our most abundant vital resources. Research data reveals that mineral
waters have an ORP of +200 mV, slightly lower than the +400 mV measured for
ordinary tap water. We can say that at least mineral water is marginally
better than tap water from the viewpoint of ORP. Compared to any processed
water for sale, however, Ionized Water with its reduction potential of -250
to -300 mV is beyond comparison due to its ability to scavenge active oxygen
radicals.
So, in this acid condition we are talking
about, we aren't "acidotic" in so many words,
rather we are base deficient. This is why 80 or 90 year
old, old folks, are shrunk up, little people. They have
no mineral stores left. When all the minerals are gone,
so are we, our battery runs down.
It is just like a battery. The cells of
our body do carry a charge that can be measured as the
oxidation/reduction potential of the blood. This energy
potential decreases with aging, just as the minerals do.
We become more oxidized (so the need for antioxidants).
Both things occur because of hyper-proteinization, too
much protein.
We aren't acidotic as they say in a hospital,
in shock, when things have gone so bad that the very pH
of the blood itself begins to change, Code Blue. Rather,
in a state of latent "acidosis" we are full of
stored acid residues, residues stored in the Pishinger
space waiting for a ride out on base minerals that aren't
there. This is the latent in latent "acidosis".
Blood values have not started to change yet, so the acidosis
is stored in the tissues as it were. The tissues are acid
but technically this is not an acidosis either as the blood
appears normal.
If things get worse, this latent "acidosis" can proceed into
what is called a compensated acidosis. This means the blood pH itself
still hasn't started to change but other values in the blood have had
to change to keep the blood pH the same 7.40 that it is supposed to
be. Decompensated acidosis is when the blood pH itself is effected.
CAUSE OF CANCER & pH Herman
Aihara, in his book entitled “Acid & Alkaline”,
states that:
If the condition of our extra
cellular fluids, especially the blood, becomes
acidic, our physical condition will first manifest
tiredness, proneness to catching colds, etc.
When these fluids become more acidic, our condition
then manifests pains and suffering such as headaches,
chest pains, stomach aches, etc. According to
Keiichi Morishita in his Hidden Truth of Cancer,
If the Blood develops a more acidic condition,
then our body inevitably deposits these excess
acidic substances in some area of the body such
so that the blood will not be able to maintain
an alkaline condition which causes these areas
such as the cells to become acidic and lowers
in oxygen.
As this tendency continues, such
areas increase in acidity and some cells die;
then these dead cells themselves turn into acids.
However, some other cells may adapt in that environment.
In other words, instead of dying - as normal
cells do in an acid environment - some cells
survive by becoming abnormal cells. These abnormal
cells are called malignant cells. Malignant cells
do not correspond with brain function nor with
our own DNS memory code. Therefore, malignant
cells grow indefinitely and without order. This
is cancer.
|
if the pH of the intestines is not right,
different bacteria and eventually yeast can grow there,
dysbiosis (wrong growth), in place of the bacteria that
should be there. This causes its own set of problems.
If the environment of the intestines is not alkaline but acid, dysbiosis
(wrong growth) occurs. The gut fills with and supports the growth of
the wrong kind of bacteria, fungus, yeast, Candida sp., etc.. These
bacteria in turn generate their own acidic, toxic byproducts of metabolism
that further aggravate and maintain the already latent "acidotic" condition.
When this dys-biosis or wrong growth begins, it begins with fermentation
and as fermentation is the process of eating, metabolizing and excreting
that bacteria do, alcohol is produced. Fermentation like this can even
cause cirrhosis of the liver in patients that have never drunk alcohol
in their life. As when making wine, this fermentation process can go
'bad' and begin to rot. Vinegar and other rotten things are produced.
This vinegar acid and the other things can cause "heart burn" too,
along with the bloating and gas that come with the fermentation process
but this kind of heart burn is not from too much acid, hydrochloric
acid, it is from not enough.
In this kind of heart burn, that comes an
hour or two after you eat, other acids form, acetic acid
as in vinegar and other putrefactive acids. These acids
cause the "heart" burn. The meal is not digesting
well as with a good amount of hydrochloric acid, it is
fermenting instead. These rotten things are reabsorbed
back into the body and picked up by the blood like anything
in the gut. These rotting things in the gut just don't
make you feel well. It's why there are constipation headaches,
sleepless nights from food eaten too late to digest (nights
where undigested food just ferments and rots all night,
makes bad dreams). The skin also tries to expel such toxins,
pimples, rashes and other skin problems develop.
With this kind of "heart burn" one
hurts after eating, right away or an hour or two later,
rather than before as with an ulcer. This can burn with
reflux up the esophagus, worse while lying down, or it
can be just pressure over the whole abdomen from the gas.
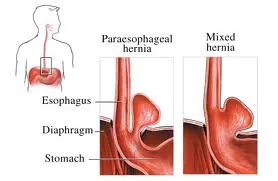
This gas can actually push the stomach through the diaphragm
into the lung cavity, producing a hiatal hernia.
The
Symptoms of Being Acid
The acidity, the pH of the body, it's
fluids and cells, is the most important homeostatic or
balancing act the body has to perform. The acidity of the
blood has to remain exactly the same all the time. The
fact that we are alkaline beings by design but acid generating
beings by function makes this the most basic function the
body has to perform, no pun intended, besides and including
breathing and pumping one's blood around. As we become
more and more acid, accumulate and store more acids in
our connective tissues this is what happens;
A. First, there is an increased sense of well being from the "stimulatory" reaction
of the bodies regulatory system that operates in high gear to
process the excess acid.
B. The patient therefore believes her or his self to be totally well.
C. This type of person tends to be an over achiever, active, always
running.
D. The person is overly ambitious due to the acidic irritation of the
nerves.
E. Later, as the process progresses the patient becomes;
1. irritable and difficult to please
2. exhausted, fatigued
3. listless and inability to get anything done
4. constantly finds fault
5. sees only the pessimistic side of life
6. can't sleep restfully
7. wakes tired in the A.M.
8. generalized aches and pains
9. I. loss of appetite or ravenous hunger
10.J. obstipation (difficulty moving bowls) to constipation gallbladder
pains and frequent headaches
11.frequent redness of the nose or parts of the nose
12.hardness and pain of the neck and shoulder muscles with pressure,
and pain of the back of the head nerves with pressure
13.often coated tongue and halitosis, enlarged tonsils
14.moist hands with poor blood supply, cold hands, pale to white
15.tendency to sweat, tendency to development of skin rashes
16.susceptibility to colds and bronchitis with large mucous secretions
as an attempt to rid the body of acid, the excretion and reaction
phases of Homotoxicology
17.women tend to be pale with scant, heavy or irregular periods
18.blood pressure tends to be lower at first
19.The Indicin-Test of the Urine (see below) is usually positive. This
is a test for rotten products in the intestine that are reabsorbed
by the
blood stream and re-excreted out the urine when the intestines are
in a dysbiotic condition, when abnormal bacteria are growing there
because of the latent acidosis
20.shows aging as the sodium is depleted from the body fluids and potassium
from muscles causing wasting and weakness, and then
calcium from the bones which is osteoporosis, arthritis and the like.
|
|
Top of
the Line Waterproof pH Meter
Ideal for all pH testing, water purification
applications, wastewater regulation, aquaculture,
hydroponics, colloidal silver, labs & scientific
testing, pools & spas, .
FEATURES
• Measures pH and Temperature
• Auto-ranging three point calibration with digital fine tuning
• Includes storage solution in a sponge embedded in a clear cap
• Waterproof housing (IP-67 rating)
• Simultaneous temperature display
• Measurement Range: 0-14 pH
• Digital automatic calibration (one point), with digital fine tuning
• Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC)
• Auto-off function, data-hold function and low-battery indicator
• Display: large and easy-to-read LCD screen includes simultaneous temperature
reading
• Factory Calibrated: The PH-200 meter is three-point checked and factory
calibrated to pH 7.0. It can be re-calibrated to any point in its range with
digital calibration using the push buttons.
More Information
|
Testing Your
PH :
1. Saliva test upon waking. First thing in the morning right when you
get out of bed, lick the end of you ph meter with saliva. Note down
that pH number. Do this before brushing your teeth, drinking, smoking,
or even thinking of eating any food. This
pH should be 6.8.
2. Then test your second urine of the morning.
The urine stored in your bladder during the night, that
is ready to be eliminated when you get up, should be acid
so you don't want to test that. Drain your bladder in the
morning, the last time you get up if you get up during
the night and then see what that urine pH is. Again, record
this number. This number should be the pH of your urine
after you got rid of your acid load from the day before.
The acids should be gone the second time you go to the
bathroom so your urine pH should be around 6.8
also.
3. Eat breakfast, an apple will do, anything,
and five minutes after breakfast check your saliva again.
Write this number down also. This number should go up from
what it was before you ate, the more the better.
4. and 5. Then check your urine pH between
meals, i.e. between breakfast and lunch and between lunch
and dinner. The pH should always be 7.0
to 8.5, a couple of hours after meals.
These five
tests show the following:
1. How well your digestive system dealt
with what you ate the night before, i.e. the AM urine pH.
These numbers may change from day to day depending on what
you did eat the night before.
2. How well we treat ourselves in general, i.e. how "strong" the
liver is. This is the AM saliva pH. This number shows the overall state
of our health, the condition of the alkaline reserve of our bodies
which reflects the diet we have eaten over the last months to years.
This number stays rather constant and will only change after some work
has been done in re-mineralizing the body.
Since the saliva pH is an indicator of intracellular
pH, saliva pH readings should never be below the pK of
the phosphate buffer
system, 6.8. . The most accurate reading of saliva pH is recorded immediately
upon awakening--after sleeping at least five hours and before brushing
the teeth. It is during sleep that the body removes waste and is in
an anabolic state restoring and replenishing the body.
If the patient has a saliva pH of 5.5 at
this time and only 5.6 after eating, you know that this
person has no alkaline reserve and that his body is devoid
of the minerals necessary to process food properly--his
body cannot adequately respond to the physiological crisis
of handling food.

3. The pH of your saliva after you eat gives
an indication of what the mineral reserves of your body
are (the pH number should increase
after you eat). My son just thought of a lemon for a minute and the
pH of his saliva went up a whole point. He had enough reserve
minerals, which are basic, to pull into his digestive system to begin
the digestive process.
The ideal saliva pH pattern is 6.8 on awakening,
7.0 before eating and 8.5 following breakfast. Besides
just thinking of a lemon one can eat one. This is a simple
test that can be done at most any time of the day. It too
checks the adequacy of the alkaline reserve of the body.
When a healthy person with adequate alkaline reserves takes
a bite of highly acid lemon, the saliva pH drops sharply
for an instant but returns almost immediately to pH 8.5.
The more acidic the food that is eaten, the more rapid
the response of the alkaline reserve, and the higher the
saliva pH should be following a meal.
4. The pH's of the urine between meals should
be kept in the basic range, pH 7.0 to 8.5. After one eats,
the stomach generates the necessary acid to digest the
food. While doing this, it also performs the opposite action,
i.e. it makes an equivalent amount of base or stream and
delivered to the alkaline glands of the body, the saliva,
the pancreas and the liver. The maximum amount of base
in the blood and therefore in the urine occurs one to two
hours after you eat.
This rhythm of the acid and base flow of
the body, is called by Frederick F Sander, the Base-floods
and the Base-tides of the Acid-Base household. This information
is from, The Acid-Base Household of the Human Organism
and its cooperation with the nail circulation and the rhythm
of the Liver, Frederick F. Sander, about 1930, translated
from the German by Robert Miller, D.C. This book is not
yet in
print in English.
Actually the body fluids and therefore the
urine is most acid at 2:00 A.M. (pH 5.0 to 6.8) in the
morning (the base tide) and most alkaline at 2:00 P.M.
(pH 7.0 to 8.5) in the afternoon (base flood)." The
ideal pH numbers depend on the time of day. Plotted on
a curve it looks like the double hump of the back of a
camel. Two times a day the urine should be alkaline and
that is the top of the humps and corresponds to 10 A.M.
and 2 P.M., the alkaline tide after meals. During the rest
of the day the pH should be between 6.6 and 6.8. This is
optimal urine. The first urine in the morning should be
more acidic because of the decalcification that takes place
during the night."
If all the acids are not all flushed out during the night they accumulate,
day after day. The cycle of chronic disease begins. It effects
different people in different ways; heart disease in one, arthritis,
osteoporosis, stones, ulcers, cancer, in others.
If what you are doing to get better
isn't working, if you are sick, be it with modern allopathic
medicines or any of the alternative, complementary therapies,
it is probably because you haven't dealt with this acid
problem, first.
THE
TREATMENT OF BEING ACID
Source
 |
ORP testing,
FEATURES
•
Measures Oxidation Reduction Potential (Redox) and
Temperature
•
Auto-ranging calibration with digital fine tuning
•
Includes storage solution in a sponge embedded in
a clear cap
•
Waterproof housing (IP-67 rating)
•
Simultaneous temperature display
•
Digital Calibration (push button)
•
Auto-off function, data-hold function and low-battery
indicator.
•
Display: large and easy-to-read LCD screen includes
simultaneous temperature reading.
•
Replaceable Sensor (model SP-O2)
•
Factory Calibrated: The ORP-200 meter is factory
calibrated to +92 mV The meter can be easily recalibrated
with digital calibration using the push buttons,
rather than a screwdriver.
•
Includes a cap, batteries, and lanyard
Specifications
ORP Range: -999 to +1000 mV
Temperature Range: 0-80°C; 32-176°F
Resolution: 1 mV; Temperature resolution is 0.1°C/F
Accuracy: 0.5% (+/-2mV)
Calibration: Digital calibration by push button.
Housing: IP-67 Waterproof (submersible; floats)
Power source: 3 x 1.5V button cell batteries (LR44
or equivalent; included)
Dimensions: 18.5 x 3.4 x 3.4 cm (7.3 x 1.3 x 1.3
inches)
Weight: 96.4 g (3.4 oz)
|
MONITOR
YOUR "PH" DAILY
Portable
PH Meter Monitor

To Receive these Amazing free newsletters click
here
|
|
Top of
the Line Waterproof pH Meter
Ideal for all pH testing, water purification
applications, wastewater regulation, aquaculture,
hydroponics, colloidal silver, labs & scientific
testing, pools & spas, .
FEATURES
• Measures pH and Temperature
• Auto-ranging three point calibration with digital fine tuning
• Includes storage solution in a sponge embedded in a clear cap
• Waterproof housing (IP-67 rating)
• Simultaneous temperature display
• Measurement Range: 0-14 pH
• Digital automatic calibration (one point), with digital fine tuning
• Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC)
• Auto-off function, data-hold function and low-battery indicator
• Display: large and easy-to-read LCD screen includes simultaneous temperature
reading
• Factory Calibrated: The PH-200 meter is three-point checked and factory
calibrated to pH 7.0. It can be re-calibrated to any point in its range with
digital calibration using the push buttons.
More Information
|
How much
water do you need?
The equivalent of 8 cups of water
for women and 12 cups of water for men is the minimum
amount of fluid recommended daily to replace water
losses under conditions of moderate activity, mild
temperature and altitude |
Drinking
From this Water flask Daily will help keep your Body
Alkaline
Can
YOU Benefit from Hydrogen Water
The
Ultimate Anti-Oxidant?
 |
Introducing
our Latest Hydrogen Water Generator at
a realistic price
NEW - provide strong antioxidant
hydrogen-rich water.
Portable - Use it anywhere, anytime
to produce fresh hydrogen-water!
Specification:
Power Source CD12V / 1A
Capacity: 0.380ml
Hydrogen water producing: 3 minutes, 5 minutes and 10 mins Dissolved
Hydrogen : 0.6ppm - 1.0ppm
PH balance: 7.6 (slightly more alkaline, stabilizing the dissolved
hydrogen)
ORP : -250 to -550 (reducing/antioxidant)
High Quality Japanses mechanism
Special introductory Price
More
Info here
|
Make
Hydrogen Water for the Whole Family
|
 |
Water
Ozenator Negative Ionizer Combo Unit
1 Water Ozenator Negative
Ionizer Combo Unit -
2 Air stone
3 Silicone Tubing
4 Remote
5 Instructions
|
| |
|
|
|
Ozone
Generator
1 500 MGH Ozone Generator
2 Air stone
3 Silicone Tube
4 Power Adapter
5 Instructions
|
| |
|
|
|
Finger
Tip Oximeter
Blood Oxygen levels low?
FingerTip Oximeter
CE Approved assorted colors
Accurate oxygen saturation and pulse rate data in seconds
Easy to use; automatically turns on/off with finger insertion/removal
Compact size fits easily into a pocket
|
 Water
not only provides the medium to make these life sustaining reactions
possible, but water itself is often an important reactant or product
of these reactions. In short, the chemistry of life is water chemistry.
Water
not only provides the medium to make these life sustaining reactions
possible, but water itself is often an important reactant or product
of these reactions. In short, the chemistry of life is water chemistry. Standing
alone, the hydrogen atom contains one positive proton at its core
with one negative electron revolving around it in a three-dimensional
shell. Oxygen, on the other hand, contains 8 protons in its nucleus
with 8 electrons revolving around it. This is often shown in chemical
notation as the letter O surrounded by eight dots representing 4
sets of paired electrons.
Standing
alone, the hydrogen atom contains one positive proton at its core
with one negative electron revolving around it in a three-dimensional
shell. Oxygen, on the other hand, contains 8 protons in its nucleus
with 8 electrons revolving around it. This is often shown in chemical
notation as the letter O surrounded by eight dots representing 4
sets of paired electrons. The
shells of the hydrogen atoms, because their electrons are closer
to the oxygen, take on a small electropositive charge. This means
water molecules have a tendency to form weak bonds with water molecules
because the oxygen end of the molecule is negative and the hydrogen
ends are positive.
The
shells of the hydrogen atoms, because their electrons are closer
to the oxygen, take on a small electropositive charge. This means
water molecules have a tendency to form weak bonds with water molecules
because the oxygen end of the molecule is negative and the hydrogen
ends are positive. To
illustrate water's ability to break down other substances, consider
the simple example of putting a small amount of table salt in a glass
of tap water. With dry salt (NaCl) the attraction between the electropositive
sodium (Na+) and electronegative chlorine (Cl-) atoms of salt is
very strong until it is placed in water. After salt is placed in
water, the attraction of the electronegative oxygen of the water
molecule for the positively charged sodium ions, and the similar
attraction of the electropositive hydrogen ends of the water molecule
for the negatively charged chloride ions, are greater than the mutual
attraction between the outnumbered Na+ and Cl- ions. In water the
ionic bonds of the sodium chloride molecule are broken easily because
of the competitive action of the numerous water molecules.
To
illustrate water's ability to break down other substances, consider
the simple example of putting a small amount of table salt in a glass
of tap water. With dry salt (NaCl) the attraction between the electropositive
sodium (Na+) and electronegative chlorine (Cl-) atoms of salt is
very strong until it is placed in water. After salt is placed in
water, the attraction of the electronegative oxygen of the water
molecule for the positively charged sodium ions, and the similar
attraction of the electropositive hydrogen ends of the water molecule
for the negatively charged chloride ions, are greater than the mutual
attraction between the outnumbered Na+ and Cl- ions. In water the
ionic bonds of the sodium chloride molecule are broken easily because
of the competitive action of the numerous water molecules.

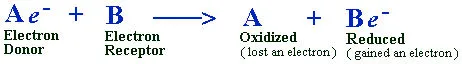

 Such
free radicals with unpaired electrons are unstable and have a high oxidation
potential, which means they are capable of stealing electrons from other
cells. This chemical mechanism is very useful in disinfectants such as hydrogen
peroxide and ozone which can be used to sterilize wounds or medical instruments.
Inside the body these free radicals are of great benefit due to their ability
to attack and eliminate bacteria, viruses and other waste products.
Such
free radicals with unpaired electrons are unstable and have a high oxidation
potential, which means they are capable of stealing electrons from other
cells. This chemical mechanism is very useful in disinfectants such as hydrogen
peroxide and ozone which can be used to sterilize wounds or medical instruments.
Inside the body these free radicals are of great benefit due to their ability
to attack and eliminate bacteria, viruses and other waste products.






 NMR
(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) analysis reveals that tap water and well water
consists of clusters of 10 to 13 2 0 molecules. Electrolysis
of water in the Ionized Water unit reduces these clusters to about half their
normal size -- 5 to 6 water molecules per cluster.
NMR
(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) analysis reveals that tap water and well water
consists of clusters of 10 to 13 2 0 molecules. Electrolysis
of water in the Ionized Water unit reduces these clusters to about half their
normal size -- 5 to 6 water molecules per cluster.



 For
example, consider the typical balanced diet of meat and vegetables. Meat
protein is metabolized into amines while nitrates from fertilizers used to
grow vegetables metabolize into nitrites in the digestive tract. These amines
and nitrites combine to form nitrosamine, a recognized carcinogen.
For
example, consider the typical balanced diet of meat and vegetables. Meat
protein is metabolized into amines while nitrates from fertilizers used to
grow vegetables metabolize into nitrites in the digestive tract. These amines
and nitrites combine to form nitrosamine, a recognized carcinogen.












