|
Clean
air is essential for good health, and this is especially
true when it comes to indoor air.
As Humans, we spend close
to 90% of our time inside; at home, at work and in
recreational environments. Most people, however, are
unaware of the effects that poor indoor air quality
can have on their health.
Synthetic building materials,
clothing and furniture coverings remove large numbers
of negative ions from the indoor environment. The
positive static charge of plastics also consumes
large quantities of negative ions. Therefore, the
negative ion count in modern buildings and homes
is often very low. |
Indoor Air Quality
What are you breathing? It is a good question to ask ourselves. All of us face
a variety of risks to our health as we go about our day-to-day lives. Driving
in cars, flying in planes, engaging in recreational activities, and being
exposed to environmental pollutants all pose varying degrees of risk. Some
risks are simply unavoidable. The good news is indoor air pollution is
one risk that you can do something about.
According to the American College of Allergies, 50%
of all illness is aggravated or caused
by polluted indoor air.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) themselves declare that indoor
air is anywhere from 2 to 10 times more
hazardous than outdoor air.
The EPA also warns us that the indoor air quality
is the number one environmental health problem.
Today's homes and buildings are built air-tight, and contain
a long list of pollution sources. As a result, natural air-cleansing agents
such as ozone and negative ions are kept
out, while contaminants are kept in.
A recent study found that the allergen level in super-insulated homes is 200%
higher than it is in ordinary homes.
Most people spend well over 90% of their time indoors. In which case, indoor
air is going to impact our health far more than outdoor air.
The EPA informs us that 6 out of 10 homes and
buildings are "sick", meaning they are hazardous
to your health to occupy as a result of airborne pollutants.
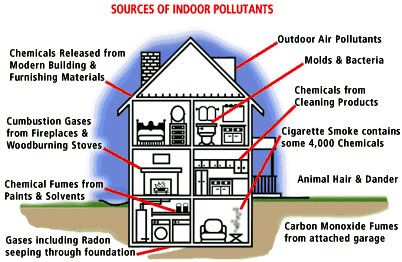
Indoor
Air Topics
 Allergies Allergies
People are not normaly born with allergies, but become allergic as a result
of contact with allergens. Allergic symptoms generally occur quickly after
exposure and they always vary in level of severity. The reaction will depend
on the person, their overall state of health, age, and the length and intensity
of exposure.
Allergies are unpleasant at the very least, but they can also trigger dangerous
reactions in certain people. Scientists use the word "allergy" to
mean any kind of altered state of the immune system when it reacts differently
to a substance as a result of previous contact.
There are two broad types
of allergies:
 Immediate
hypersensitivity is the common kind of allergy
that causes hay fever, allergic asthma, food allergies
and some drug allergies. People with this condition have
a reaction within minutes of exposure to the allergen
in question. Immediate
hypersensitivity is the common kind of allergy
that causes hay fever, allergic asthma, food allergies
and some drug allergies. People with this condition have
a reaction within minutes of exposure to the allergen
in question.
 Delayed
hypersensitivity is a peeling eczema-like
rash called "contact dermatitis" and
is triggered when an allergen comes into contact
with the skin. This type of reaction is much slower
and usually takes two days to become obvious. Delayed
hypersensitivity is a peeling eczema-like
rash called "contact dermatitis" and
is triggered when an allergen comes into contact
with the skin. This type of reaction is much slower
and usually takes two days to become obvious.
 Carbon
Monoxide Carbon
Monoxide
Carbon monoxide is a colourless, odourless gas that reduces the amount of oxygen
in the blood. Low levels over long periods of time are dangerous, and high
levels can cause unconsciousness and even death. To keep your indoor air clean
and healthy, make sure that fuel-burning devices are well vented. Beware of
Idling vehicles in garages that are attached to homes or buildings;
 At
low levels, symptoms include headaches, tiredness,
shortness of breath and impaired motor functions. These
symptoms sometimes feel like the flu. At
low levels, symptoms include headaches, tiredness,
shortness of breath and impaired motor functions. These
symptoms sometimes feel like the flu.
 At
high levels, or if people are exposed
to low levels for long periods of time, people
can experience dizziness, chest pain, tiredness,
poor vision and difficulty thinking. At
high levels, or if people are exposed
to low levels for long periods of time, people
can experience dizziness, chest pain, tiredness,
poor vision and difficulty thinking.
 At
very high levels, carbon monoxide can
cause convulsions, coma and even death. At
very high levels, carbon monoxide can
cause convulsions, coma and even death.
No smoking please! Since tobacco smoke
is a source of carbon monoxide, don't let people
smoke indoors.
 Formaldehyde Extensive
reviews of formaldehyde emissions sources have been
published by the World Health Organization (WHO 1989),
and Environment Canada and Health Canada (2001). Sources
that influence indoor levels of formaldehyde can be
divided into two broad categories: combustion and off-gassing.
Combustion sources include cigarettes and other tobacco
products, and open fireplaces. Off-gassing sources
include wood products such as particle board and other
building materials made with adhesives containing formaldehyde
as well as some varnishes, paints, carpeting, drapes
and curtains. Formaldehyde Extensive
reviews of formaldehyde emissions sources have been
published by the World Health Organization (WHO 1989),
and Environment Canada and Health Canada (2001). Sources
that influence indoor levels of formaldehyde can be
divided into two broad categories: combustion and off-gassing.
Combustion sources include cigarettes and other tobacco
products, and open fireplaces. Off-gassing sources
include wood products such as particle board and other
building materials made with adhesives containing formaldehyde
as well as some varnishes, paints, carpeting, drapes
and curtains.
Results from studies carried out in Canada since the early
1990s consistently indicate that formaldehyde concentrations
in Canadian homes range between 2.5 and 88 µg/m3with
an average between 30 and 40 µg/m3(Health Canada
2005).
When formaldehyde is present in the air at levels exceeding
0.1 ppm, some individuals may experience health effects
such as watery eyes; burning sensations of the eyes, nose,
and throat; coughing; wheezing; nausea; and skin irritation.
Some people are very sensitive to formaldehyde, while others
have no reaction to the same level of exposure.
Epidemiological studies on the effects of chronic formaldehyde
exposure consistently found respiratory and allergic effects
at levels below 123µg/m3(Health Canada, 2005). In
one study, formaldehyde levels in homes were associated
with increased risk of atopy, after ruling out confounding
from other indoor air pollutants (Garrett, et al., 1999).
In another study, formaldehyde levels were significantly
associated with hospitalization for asthma in children
aged six months to three years,
Formaldehyde has been classified as a human carcinogen
(cancer-causing substance) by the International Agency
for Research on Cancer and as a probable human carcinogen
by the U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency
 Asthma -
Asthma is a rapidly growing public health problem. About
23 million people, including 6.8 million children, have
asthma and 12 million people report having an asthma attack
in the past year. Asthma
accounts for nearly 17 million physician office and hospital
visits, and nearly 2 million emergency department visits
each year... Asthma -
Asthma is a rapidly growing public health problem. About
23 million people, including 6.8 million children, have
asthma and 12 million people report having an asthma attack
in the past year. Asthma
accounts for nearly 17 million physician office and hospital
visits, and nearly 2 million emergency department visits
each year...
 Mold Molds
are part of the natural environment. Molds reproduce by
means of tiny spores; the spores are invisible to the naked
eye and float through outdoor and indoor air. Mold may
begin growing indoors when mold spores land on surfaces
that are wet. There are many types of mold, and none of
them will grow without water or moisture. Mold Molds
are part of the natural environment. Molds reproduce by
means of tiny spores; the spores are invisible to the naked
eye and float through outdoor and indoor air. Mold may
begin growing indoors when mold spores land on surfaces
that are wet. There are many types of mold, and none of
them will grow without water or moisture.
Molds can be found almost anywhere; they
can grow on virtually any organic substance, as long as
moisture and oxygen are present. There are molds that can
grow on wood, paper, carpet, foods, and insulation. When
excessive moisture accumulates in buildings or on building
materials, mold growth will often occur, particularly if
the moisture problem remains undiscovered or unaddressed.
It is impossible to eliminate all mold and mold spores
in the indoor environment. However,
mold growth can be controlled indoors by controlling Air
and moisture indoors.
| Most all particles in the air have a
positive charge or are positively ionized, while
negative ions have a negative charge. Negative
ions are drawn to these positively charged particles
by magnetic attraction to one another. When there
is a high enough concentration of negative ions
in the air, they will attract to floating particles
in large numbers. This causes the particle to become
too heavy to remain airborne. As a result, the
particle will drop out of the air, keeping them
out of the breathing zone and out of the respiratory
system where it can trigger breathing and health
problems. |
 Radon You
can't see radon, you can't smell it or taste it, but it
may be a problem in your home. Radon is estimated to cause
many thousands of deaths each year. That's because when
you breathe air containing radon, you can get lung cancer.
In fact, the Surgeon General has warned that radon is the
second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States
today. Radon is a cancer-causing natural radioactive gas
that you can’t see, smell or taste. Its presence
in your home can pose a danger to your family's health.
Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers.
Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in America
and claims about 20,000 lives annually. Radon You
can't see radon, you can't smell it or taste it, but it
may be a problem in your home. Radon is estimated to cause
many thousands of deaths each year. That's because when
you breathe air containing radon, you can get lung cancer.
In fact, the Surgeon General has warned that radon is the
second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States
today. Radon is a cancer-causing natural radioactive gas
that you can’t see, smell or taste. Its presence
in your home can pose a danger to your family's health.
Radon is the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers.
Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in America
and claims about 20,000 lives annually.
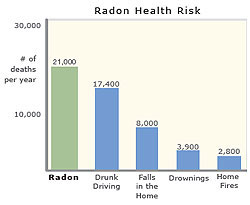
| Radon is estimated to cause about 21,000
lung cancer deaths per year, according to EPA's 2003
Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003).
The numbers of deaths from other causes are taken from
the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's 1999-2001
National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Report
and 2002 National Safety Council Reports. |
 |
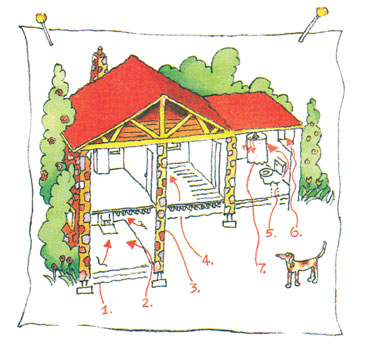 |
RADON GETS IN THROUGH:
Cracks in solid floors
Construction joints
Cracks in walls
Gaps in suspended floors
Gaps around service pipes
Cavities inside walls
The water supply
|
| There are two main sources for the radon
in your home's indoor air, the soil and the water supply.
Compared to radon entering the home through water,
radon entering your home through the soil is usually
a much larger risk.
The radon in your water supply poses an inhalation
risk and an ingestion risk. Research has shown
that your risk of lung cancer from breathing radon
in air is much larger than your risk of stomach
cancer from swallowing water with radon in it.
Most of your risk from radon in water comes from
radon released into the air when water is used
for showering and other household purposes.
|
What are Negative
Ions?
Negative ions are odorless, tasteless, and
invisible molecules that we inhale in abundance in certain
environments. Think mountains, waterfalls, and beaches.
Once they reach our bloodstream, negative ions are believed
to produce biochemical reactions that increase levels of
the mood chemical serotonin, helping to alleviate depression,
relieve stress, and boost our daytime energy.
| In nature, ions are formed in a variety
of ways, such as UV light, airflow friction, lighting,
falling water and by plants. |
Benefits of Negative Ions
Negative ion generators (negative ionizers) have been
used for years to help rid closed indoor environments of
allergens such as dust particles, animal dander, pollen,
mold spores, cigarette smoke, cigar smoke, PM10 particulate
matter, etc. floating in the air.
Vitamins of the Air--Generally speaking, negative ions increase the flow of
oxygen to the brain; resulting in higher alertness, decreased drowsiness, and
more mental energy," says Pierce J. Howard, PhD, author of The Owners
Manual for the Brain: Everyday Applications from Mind Brain Research and director
of research at the Center for Applied Cognitive Sciences in Charlotte, N.C.
 |
THE IMPORTANCE OF OXYGEN
The air we breathe contains oxygen. Oxygen is the
spark of life. Just as a fire can’t burn without oxygen our cells can’t produce heat and energy
without oxygen. Oxygen is extracted from the air we breathe by the lungs. It
passes into the blood vessels that surround the lungs and is carried to all
the cells of the body by the blood. Most of the oxygen is carried by the red
blood cells, though some of it is carried by the water in the blood. A deficiency
of water means reduced oxygen delivery by the blood. So important is oxygen,
that even where optimum water, protein, vitamin and mineral intake exists,
ill health will still exist if there’s an oxygen deficiency. Under-breathing
is epidemic among adults.
|
Purify the Air--protect against germs in the air, resulting
in decreased irritation due to inhaling various particles
that make you sneeze, cough, or have a throat
irritation.
As parents, we’ve all been keeping our child’s things clean so
that our family can lead a happy, healthy life. But did you ever think to sterilize
your air?
Negative Ions for the Brain--High concentrations of negative ions are essential
for high energy and positive mood (Thayer, 1996)
Effects of Negatively Charged Fresh Air
 Improved
sense of well being Improved
sense of well being
 Increased
rate and quality ofgrowth in plants and animals Increased
rate and quality ofgrowth in plants and animals
 Improved
function of the lung’sprotective cilia Improved
function of the lung’sprotective cilia
 Tranquilization
and relaxation(decreased anxiety) Tranquilization
and relaxation(decreased anxiety)
 Lowered
body temperature Lowered
body temperature
 Lowered
resting heart rate Lowered
resting heart rate
 Decreased
survival of bacteriaand viruses in the air Decreased
survival of bacteriaand viruses in the air
 Improved
learning in mammals Improved
learning in mammals
 Decreased
severity of stomach. Decreased
severity of stomach.
How ozone
purifies the air

Ozone oxidizes airborne pollutants, then reverts back
to oxygen, transforming polluted air to pure and refreshened
air.
Here is how the process works:
Oxygen molecules (O1 and O2) are converted to ozone (O3)
by either a high-voltage electrical charge (such as from
lightning), or by ultraviolet light (such as from the sun
rays).
One oxygen atom (O1) splits off from the ozone molecule, and reacts with other
particles when it comes within range of a particle and/or pollutant. Ozone
is highly reactive, so it never fails to initiate this reaction with other
particles.
As the 2nd most powerful oxidant in existance, the single
oxygen atom proceeds to "oxidize" the particle
it reacts with. This means it burns the particle, which
changes its physical properties. As a result, the particle
will no longer be toxic, and will no longer be able to
reproduce if it is biological. In other words, the particle
becomes completely harmless.
When the single oxygen (O1) molecule oxidizes the particle,
it too is destroyed. This leaves behind the O2 it split
away from, or pure and clean oxygen.
"The large majority of those infectious
microbes that cause us so much illness and pain are
ANAEROIC...a
big word that means they live and proliferate best
in environments where there is LITTLE OR NO OXYGEN."
- Ed McCabe: Oxygen Therapies: A New Way of Approaching Disease |
Professional Studies
The Refrigeration Service Engineers Society has reported
that electric-arc welders exposed to ozone levels of 0.2
to 0.3 ppm (parts per million) for a decade showed no adverse
effects. The Surround Air Ionizers produce between 0.02
to 0.04 ppm of ozone. Also, according to the 1961 Encyclopedia
of Chemical Technology, "During the 80-year history
of the large scale usage of ozone, there has never been
a human death attributed to it." To this day, there
has still never been a single human death or incident of
harm attributed to ozone.
This despite the fact that ozone was widely used in hospitals
during the first half of the 20th century, and is still
widely used in European hospitals. In addition, millions
of ozone air purification systems are in use worldwide,
both commercially and residentially.
In addition, the smell of ozone will become unpleasant and obnoxious well before
reaching harmful levels, serving as a built-in and self-policing safety mechanism.
If this happens, you know to make an adjustment (i.e. adjust setting of machine,
increase air flow, place in more open/larger area).
However, at proper levels (0.02 ppm to 0.05 ppm), it will
have a pleasant and clean smell to it, reminiscent of the
smell outside after a lightening storm.
| Since high levels of negative ions are
needed for good health, many people put ionisers
in bedrooms and major activity rooms..... |
The positive
health effects of negative ions have been known for
almost a hundred years.
Negative ions increase the flow of oxygen
to the brain; resulting in higher alertness, decreased
drowsiness, and more mental energy," says Pierce J.
Howard, PhD, author of The Owners Manual for the Brain:
Everyday Applications from Mind Brain Research and director
of research at the Center for Applied Cognitive Sciences
in Charlotte, N.C.
" They also may protect
against germs in the air, resulting in decreased irritation
due to inhaling
various particles that make you sneeze, cough, or
have a throat irritation.
And for a whopping one in three of us who are sensitive to their effects, negative
ions can make us feel like we are walking on air. You are one of them if you
feel instantly refreshed the moment you open a window and breathe in fresh,
humid air.
You may be one of them if you feel sleepy when you are around an air-conditioner,
but feel immediately refreshed and invigorated when you step outside or roll
down the car window," Howard says. "Air
conditioning depletes the atmosphere of negative ions, but an ion generator
re-releases the ions
that
air conditioners remove."
The
bactericidal effects of negative ions in air
The use of negative ions to improve indoor
air quality has attracted increasing attention in recent
years. Although the physical action of air ionisers is
accepted, there is still debate over their apparent biocidal
action. A recent clinical trial in an intensive care unit
suggested that air ionisers may have a role in reducing
the transmission of infection in healthcare environments1
and several authors have reported that ions inhibit the
growth of a range of microorganisms. A further understanding
of this process was gained through bench scale experiments
exposing sessile cultures to positive and negative ions2.
The aim of the work presented here was to follow on from
the bench scale experiments to investigate the efficacy
of negative ions with aerosolised microorganisms.
|
OZONATED WATER
Rinse all your fruit and vegetables
with ozonated water to kill bacteria and pesticides.
Clean babies bottles etc. using the ozonated water
to sterilise. Drink ozonated water for O3 therapy.
|
| |
|
|
Portable Ultrasonic
Atomized Nebuliser
Is There Some Other Way To Get Colloidal
Silver Into the Body, Quickly and Effectively?
Inhalation of Silver Nanoparticles Results in "Miraculous" Protection
Against colds, flu, pneumonia and other upper respiratory
infections
Automatic shut-off when empty.
Quiet treatment
Compact and portable
Lightweight (under 0.5kg)
Operating Voltage 12V AC/DC Adapter
Mask
|
| |
|
|
Are you Getting Enough Oxygen ?
Oxygen is one of the most important
keys to good health, but not everyone is aware of
it. Currently scientists are examining the role oxygen
starvation plays in the development of disease.
CE Approved Black only
Accurate oxygen saturation and pulse rate data in
seconds
Easy to use; automatically turns on/off with finger
insertion/removal Compact size fits easily into a pocket
|
| |
|
|

