Brain May Grow New Cells Daily
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Forum
Join a Discussion on How the Brain Works
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
By
NICHOLAS WADE
n a new challenge to the longstanding belief that adults never
generate new brain cells, biologists at Princeton University have found that thousands
of freshly born neurons arrive each day in the cerebral cortex, the outer rind
of the brain where higher intellectual functions and personality are centered.
Though based on research in monkeys, the finding is likely to prove true
of people, too.
If so, several experts said, it may overturn ideas about
how the human brain works and open new possibilities for treating degenerative
brain diseases.
MORE GRAY MATTER
Researchers have found that
the brains of macaque monkeys produce new brain cells that migrate to the cerbral
cortex, where higher functioning is centered.
Frontal view of brain
1. Neural stem cells, neurons in their early stage of development, are
produced in the central area of the brain.
2. The neurons develop as they
migrate.
3. The mature neurons reach the outer cortex, the location of
advanced functions in the brain.
Source: Science
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
If the new brain cells, or neurons, are involved in memory and learning --
perhaps with each day's batch of new cells recording that day's experiences --
scientists will have to make major revisions in the longtime view that the adult
brain's neurons are static in number and that memory is stored only in the way
they interconnect.
In addition, if the brain's cells are in constant turnover,
as the new finding suggests, physicians may discover ways to use the brain's natural
regeneration system for replacing cells that are lost in diseases of aging.
The
discovery, by Elizabeth Gould and Charles G. Gross, is reported in Friday's issue
of the journal Science.
The belief that the adult brain does not make new
cells rested on careful, well-known studies by Pasko Rakic of Yale University,
who looked for the formation of new neurons in the monkey brain and found none.
But the Princeton work is likely to be convincing, because it builds on
previous reports of brain cell turnover, notably by Fernando Nottebohm of Rockefeller
University, who showed that canaries grow new neurons to learn new songs, and
recent studies showing that new cells are formed in the hippocampus, a brain region
where initial memories of faces and places are formed.
"The scientific
community can easily believe something it is 50 percent ready to absorb, but not
something that comes out of left field," said Eric R. Kandel, a leading neuroscientist
at Columbia University. "But here, we are prepared for it."
Kandel
compared the likely change in view to the paradigm shifts described by the historian
of science Thomas Kuhn as occurring when one major scientific theory is replaced
by another.
Although the new study was done in macaque monkeys and has
yet to be confirmed in humans, as fellow primates monkeys are usually quite predictive
of what occurs in people.
Gould, who has studied new cell formation in
the hippocampus, and Gross, an expert on the cerebral cortex, injected macaques
with a chemical that is incorporated in the new DNA formed when a cell divides.
They found that a stream of new neurons were generated in the monkeys'
brains in a zone just above the brain's fluid-filled central chambers. This zone
was recently identified by other scientists as the home of the brain's stem cells,
the source cells from which an organ is replenished.
The new neurons migrated
toward the cortex, matured and sent out axons to make connections with other brain
cells, the Princeton biologists found.
The researchers looked for new neurons
in four areas of the cortex, and found them in three areas where memories are
known to be stored: the frontal cortex, used for decision-making, and two areas
on the side of the brain used for visual recognition.
No new neurons were
detected in the fourth area, the striate cortex, a region at the back of the head
that simply processes visual information from the eyes and passes it on to other
parts of the cortex.
Whatever the new cells are doing in the cortex, they
affect regions of the brain that are central to human thought and identity. The
Princeton work, said Ronald D. G. McKay, an expert on brain stem cells at the
National Institutes of Health, "places new neurons in the region of the brain
involved in the highest level of personality: it's the frontal cortex that is
important in determining who you are in a very human way."
Gould said
it was possible that the new neurons arriving in the cortex would be particularly
sensitive to recording information for a certain period while they matured.
"They
would become integrated in the circuitry and represent the information being learned
at that particular time," she said, after which they would not record anything
more.
In other words, the conveyor belt of new neurons might record successive
days' experiences almost like a moving tape.
"We know the characteristic
of memory is that events are tagged with times," Gross said. "We have
no idea how that is done. But since we have now shown there are new cells added
every day, which cover a spectrum of ages, these cells could possibly provide
the substrate for the temporal dimension of memory."
Kandel, of Columbia
University, said the idea was perfectly possible, given how little was now known
about the brain's system for ultimate long-term memory storage.
"How
do you distinguish the memory of 20 years ago from the memory of 30 years ago?
You would have to mark the birthday of the cell in some way," Kandel said,
suggesting that the train of new neurons offered a plausible mechanism whereby
the brain might somehow do this.
The notion that new memories are stored
in a train of new nerve cells was advocated in the 1960's by Joseph Altman, then
of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. But his proposal was not widely
accepted. And when Rakic, an authority on neuron formation in the embryonic monkey
brain, reported in 1985 that no new neurons were formed in the adult monkey's
brain, this became the accepted view.
Even when Gould and others showed
recently that new cells were formed in the hippocampus, Rakic argued that this
was a primitive area of the brain -- even reptiles have a hippocampus -- and that
brain organs acquired more recently in evolution, like the primates' cerebral
cortex, would not be expected to behave the same way.
Gould said it was
this argument that had made her determined to look for new cells being formed
in the cerebral cortex, despite the expense of doing work on monkeys and the risk
in "redoing an experiment that a very well respected person," Rakic,
had already performed.
Rakic's office said he was traveling yesterday and
unavailable for comment.
If indeed the brain is constantly renewing the
cells in its cortex, hippocampus and maybe other areas, the prospects for learning
how to repair the aged or damaged brain begin to look much more hopeful.
"Degenerative
diseases of the brain are really defined by loss of nerve cells," Kandel
said. Though diseases like Parkinson's affect specific areas of the brain, it
might become possible to channel young new neurons into the areas of disease.
"This is pie in the sky," he said, "but at least there is now the
possibility of thinking about it."
William T. Greenough, a neuroscientist
at the University of Illinois, said the Princeton work created a "whole new
ball game" for addressing brain diseases, by harnessing the brain's own restorative
potential.
The Princeton biologists plan to follow up their discovery by
blocking the formation of new neurons in monkeys' brains and seeing what happens.
If the new neurons are essential for memory and learning, then serious deficits
should appear in the monkeys' performance.
The researchers as yet have
no idea whether the loss of brain cells and the generation of new ones are separate
events or part of the same cycle.
"Our discovery," Gross said,
"suggests more questions than answers."
Salk
Institute Study Finds Brains Can Grow New Cells
Brain nutrient can
help maximize memory.
by Ronald M. Lawrence, M.D., Ph.D.
According to
a recently completed animal study conducted by the Salk Institute, it turns out
that regular exercise helps an "old brain" build new brain cells (Van
Praag 2002). Just as importantly, researchers have found that the daily use of
powerful brain nutrients can support the brain by boosting membrane function (Kidd
1998). It's all good news for aging brains.
The Salk Institute study, published
in the science journal Nature, found that in mice, new brain cells were generated
in the hippocampus, the area of the brain responsible for learning and memory.
After only four months, these new brain cells were found to mature into functional
neurons (Van Praag 2002).
The researchers don't know what these new brain
cells actually do, but they hope to someday replicate the effects in other areas
of the brain. Imagine the implications for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's
or for diseases such as stroke that destroy brain cells (Newswise 2002).
Nutrient
to Assist Thinking and Memory
For the present, there is encouraging news about
maintaining brain health, especially through the use of the naturally occurring
compound phosphatidylserine (PS). PS is a key building block for brain cells.
Specifically, it helps maintain the integrity and the fluidity of brain cell membranes,
which are a kind of sheath that has many functions. Cell membranes protect the
cells while simultaneously letting nutrients in and waste products out, and their
flexibility is crucial for enhancing swift communication between neurons (Kidd
1998).
BRAIN CELL GROWTH AFFECTED BY
STRESS
For years, neurobiologists clung to a fundamental truth:
as animals and people reach adulthood, they lose brain cells and they never grow
new ones. There were a couple of exceptions such as birds and rats, but the thought
was that these were peculiarities of nature and not evidence of a general principle.
Now, in experiments that experts call amazing, that dogma has been overturned
because scientists have found that monkeys are constantly making new brain cells
in the hippocampus, an area of the brain used for forming long-term memories.Moreover,
they report, the production of new cells is squelched when the animals are under
extreme stress.
Experts say they fully expect that humans are no different
and that they, too, make new brain cells in adult life. That raises the glimmer
of a possibility of eventually treating degenerative disorders like Alzheimer's
or Parkinsons disease and injuries such as those resulting from stroke or trauma
— by prompting the brain to grow replacement cells.
It also means that
neurobiologists must rethink basic notions of the way the brain changes with learning
or life experiences.
Dr. Elizabeth Gould of Princeton University, Dr. Bruce
S. McEwen of Rockefeller University in Ncw York and their colleagues investigated
using marmoset monkeys, adding two tracer chemicals to the animals' brains: one
that labeled cells that were dividing — the process that gives rise to new
cells and one that labeled mature nerve cells. Cells that were born during adult
life and that grew into mature brain cells would be marked by both chemicals.
With
this method, the researchers looked for, and found, new cells in the animals'
hippocampuses.
Dr. Gould estimated that thousands of such cells were being
made each day. She said she suspected other cells were dying to make room for
new ones, but her study did not count numbers of dying cells.
The hippocampus
was particularly intriguing for another reason, Dr. Gould said. Earlier research
had shown that when people are under stress, the hippocampus shrinks in size.
For example, people with tumors that pour out the stress hormone cortisol have
a diminished hippocampus. So do people with recurrent depression and people with
posttraumatic stress disorder, Dr. Gould said.
It might be possible, she
reasoned, that monkeys under stress might decrease their production of new brain
cells in the hippocampus, making that area of the brain shrink.
To test
the hypothesis, Dr. Gould and her colleagues stressed monkeys by putting a male
monkey who had always lived alone into a small cage where another male was living.
The intruder was terrified and cowered in the cage, with a rapidly beating heart.
When Dr. Gould and her colleagues examined the brains of the frightened monkeys,
they found that after just one hour of this stress, the monkeys were making substantially
fewer new I brain cells.
The study is being published in The Proceedings
of the National Academy of Sciences.
As so often happens in science, the
seeds for the new view of brain regeneration were sown decades ago, but were largely
ignored.
In the 1960s, Dr. Joseph Altman, a Purdue University scientist
who is now retired, reported that rats make new brain cells throughout their lives.
The cells were in the hippocampus and in the olfactory bulb, an area used to sense
smells, he noted. "No one paid attention,"Dr. Gould said.
Twenty
years later, Dr. Fernando Nottebohm, who is head of the laboratory of animal behavior
at Rockefeller University, asked whether brain cells were being born in adult
birds. Bird brains, he noticed, grow and shrink with the seasons, swelling when
the animals need to learn new songs to attract mates and shrinking after they
had bred. He wondered whether the swelling brains during breeding seasons could
represent the actual growth of new brain cells. At the time, Dr. Nottebohm said,
he knew nothing of Dr. Altman's work.
In a series of painstaking experiments,
Dr. Nottebohm showed that birds constantly make new brain cells and that the new
cells replace old ones that die. "There was a program of constant brain rejuvenation,"Dr.
Nottebohm said.
In 1984, Dr. Nottebohm organized a meeting in New York that
he called Hope for a New Neurology A colleague at Rockefeller, Dr. Arturo Alvarez-Buylla
recalled that Dr. Nottebohm "was pushing the idea that in the adult brain,
there is no impediment to the formation of new neurons." But, Dr. Alvarez-Buylla
added, "people thought that was bordering on fantasy."Nonetheless, some
researchers persisted, showing in rats and mice and in tree shrews that new brain
cells are born throughout life, at least in the hippocampus and olfactory bulb.
Dr.
Alvarez-Buylla, for example, recently found that adult mice make 5,000 to 10,000
new brain cells each hour. The brain cells that end up in the olfactory bulb are
born on the walls of the ventricles, cavities in the brain that are called with
cerebrospinal fluid. They travel in "little trains of cells" to their
destination, he said. Those that end up in the hippocampus are born there. But
many scientists believed that monkeys and humans could not be growing new brain
cells -- that in order to store memories for a lifetime, you need a stable brain.
Dr.
Gould said. "If cells are constantly dying and new ones being produced, how
would that be possible?" Dr. Gould, however, was persuaded by the findings
on other species. ''Why not monkeys?" she asked. Others also began seeking
and finding brain regeneration in monkeys, but Dr. Gould is the first to publish
her findings.
Do we lose brain cells as we get older? Scientists know
that most of us lose brain mass as we get older. CT scans of older adults often
show some degree of cerebral atrophy - brain shrinkage. There is also research
that suggests that we lose connections between brain cells as we age. My father
is beginning to have difficulty remembering names. They usually come to him eventually,
but they do not seem to be as easily retrieved as in the past. The name is still
stored, it's just not easily accessed.
Can anything be done about this?
Are we destined to lose our faculties as we age? There is some hope on several
fronts. Recent research on Alzheimer's Disease suggests that there might some
day be a vaccine that protects us from Alzheimer's build-up of plaques and tangles
in our brains. Some studies suggest that physical exercise keeps brains healthy.
There is also research that suggests that we can keep our brains working well
by using them regularly. This is the principle behind a recent book by Lawrence
Katz, Ph.D. and Manning Rubin. Katz is a neuroscientist at Duke University who
studies brain aging. Their book, Keep your Brain Alive, describes practical exercises
that anyone can do to keep the brain working at top efficiency. Eating or brushing
your teeth with your non-dominant hand, for example, allows your brain to use
pathways that are not frequently accessed.
BRAIN MAY GROW NEW CELLS DAILY:
Princeton Study on Monkeys Challenges Long-Held View
by Nicholas Wade
In a new challenge to the long-standing belief that adults never generate
new brain cells, biologists at Princeton University have found that thousands
of freshly born neurons arrive each day in the cerebral cortex, the outer rind
of the brain where higher intellectual functions and personality are centered.
Though based on research in monkeys, the finding is likely to prove true of
people, too. If so, several experts said, it may overturn ideas about how the
human brain works and open new possibilities for treating degenerative brain
diseases.
If the new brain cells, or neurons, are involved in memory and learning --
perhaps with each day's batch of new cells recording that day's experiences
-- scientists will have to make major revisions in the long-time view that
the adult brain's neurons are static in number and that memory is stored only
in the way they interconnect.
In addition, if the brain's cells are in constant turnover, as the new finding
suggests, physicians may discover ways to use the brain's natural regeneration
system for replacing cells that are lost in diseases of ageing.
The discovery, by Dr Elizabeth Gould and Dr Charles G Gross, is reported in
today's issue of the journal Science.
The belief that the adult brain does not make new cells rested on careful,
well-known studies by Dr Pasko Rakic of Yale University, who looked for the
formation of new neurons in the monkey brain and found none.
But the Princeton work is likely to be convincing, because it builds on previous
reports of brain cell turnover, notably by Dr Fernando Nottebohm of Rockefeller
University, who showed that canaries grow new neurons to learn new songs, and
recent studies showing that new cells are formed in the hippocampus, a brain
region where initial memories of faces and places are formed.
"The scientific community can easily believe something it is 50% ready
to absorb, but not something that comes out of left field," said Dr Eric
R Kandel, a leading neuroscientist at Columbia University. "But here,
we are prepared for it."
Dr Kandel compared the likely change in view to the paradigm shifts described
by the historian of science Thomas Kuhn as occurring when one major scientific
theory is replaced by another.
Although the new study was done in macaque monkeys and has yet to be confirmed
in humans, as fellow primates monkeys are usually quite predictive of what
occurs in people.
Dr Gould, who has studied new cell formation in the hippocampus, and Dr Gross,
an expert on the cerebral cortex, injected macaques with a chemical that is
incorporated in the new DNA formed when a cell divides.
They found that a stream of new neurons were generated in the monkey's brains
in a zone just above the brain's fluid-filled central chambers. This zone was
recently identified by other scientists as the home of the brain's stem cells,
the source cells from which an organ is replenished.
The new neurons migrated toward the cortex, matured and sent out axons to
make connections with other brain cells, the Princeton biologists found.
The researchers looked for new neurons in four areas of the cortex, and found
them in three areas where memories are known to be stored: the frontal cortex,
used for decision-making, and two areas on the side of the brain used for visual
recognition. No new neurons were detected in the fourth area, the striate cortex,
a region at the back of the head that simply processes visual information from
the eyes and passes it on to other parts of the cortex.
"Transcutaneous
Electrical Stimulation for Tinnitus." By Marvin Engelberg, Ph.D.
and William Bauer, M.D. presented at the Meeting
of the Southern Section of the American Laryngological,
Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.,
New Orleans, Louisiana, January, 1985 and published
in the Laryngoscope, Vol. 95, No. 10, October,
1985.
At the Veterans Administration
Medical Center in Cleveland, Ohio, "The
use of (Alpha-Stim) electrical stimulation
to treat tinnitus was
evaluated in a two-experiment study...Eight-two
percent of the 33 ears showed improvement by
either of the two criteria. The permanence
of the improvement ranged from 20 minutes to
at least six months. Most of the subjects had
either one or two treatment sessions. Subject
2 was seen for seven treatment sessions, each
session tending to increase the duration of
improvement."
In Experiment 2, "Of
the 17 ears treated, two (subject 8, both
ears) were perceived as
not having improved by stimulation. Thus, 9
of 10 subjects (90%) corresponding to 15 of
17 ears (88%) reported the stimulation as having
improved the tinnitus. Of the 15 ears administered
the control stimulation, in only one ear did
a subject (subject 18, right ear) believe that
there had been a change."
The authors concluded that, "The
82% success rate in improvement in tinnitus
implies
a feasible treatment procedure." |
Whatever the new cells are doing in
the cortex, they affect regions of the brain that
are central to human thought and identity. The Princeton
work, said
Ronald D G McKay, an expert on brain stem cells at
the National Institute of Health, "places new
neurons in the region of the brain involved in the
highest level of personality: it's the frontal cortex
that is important in determining who you are in a
very human way."
Dr Gould said that it was possible that the new neurons arriving in the cortex
would be particularly sensitive to recording information for a certain period
while they matured.
"They would become integrated in the circuitry and represent the information
being learned at that particular time," she said, after which they would
not record anything more.
In other words, the conveyor belt of new neurons might record successive days'
experiences almost like a moving tape.
This study addresses the
question, 'can low intensity electrostimulation
applied through
the ear lobes significantly improve human learning
and performance of a psychomotor task such
as typing?' A double-blind placebo control
design was used. Seventy-eight subjects were
randomly assigned to two groups: (1) the experimental
(STIM) group which received electrostimulation
while performing a computer typing game; and
(2) the control (NSTIM) group which did not
receive TCES, but otherwise received the same
treatment as the STIM group."
The dependent measure was
the performance gain score obtained for each
subject by calculating
the score differential between the first and
second trials. Statistical analysis demonstrated
a significantly larger performance gain score
for the STIM group over the NSTIM group as
well as a significantly larger ultimate mean
performance score."
|
"We know the characteristic of memory is that events are tagged with
times," Dr Gross said. "We have no idea
how that is done. But since we have now shown there
are new cells added every day, which cover a spectrum
of ages, these cells could possibly provide the substrate
for the temporal
dimension of memory."
Dr Kandel, of Columbia University, said the idea was perfectly possible, given
how little was now known about the brain's system for ultimate long-term memory
storage.
"How do you distinguish the memory of 20 years ago from the memory of
30 years ago? You would have to mark the birthday of the cell in some way," Dr
Kandel said, suggesting that the train of new neurons offered a plausible mechanism
whereby the brain might somehow be able to do this.
The notion that new memories are stored in a train of new nerve cells was
advocated in the 1960's by Dr Joseph Altman, then of the Massachusetts Institute
of Technology. But his proposal was not widely accepted. And when Dr Rakic,
an authority on neuronic formation in the embryonic monkey brain, reported
in 1965 that no new neurons were formed in the adult monkey's brain, this became
the accepted view.
Even when Dr Gould and others showed recently that new cells were formed in
the hippocampus, Dr Rakic argued that this was a primitive area of the brain
-- even reptiles have a hippocampus -- and that brain organs acquired more
recently in evolution, like the primates' cerebral cortex, would not be expected
to behave the same way.
Dr Gould said it was this argument that had made her determined to look for
new cells being formed in the cerebral cortex, despite the expense of doing
work on monkeys and the risk in "redoing an experiment that a very well
respected person," Dr Rakic, had already performed.
If indeed the brain is constantly renewing the cells in its cortex, hippocampus
and maybe other areas, the prospects for learning how to repair the aged or
damaged brain begin to look much more hopeful.
"Degenerative diseases of the brain are really defined by loss of nerve
cells." Dr Kandel said. Though diseases like Parkinson's affect specific
areas of the brain, it might become possible to channel young new neurons into
the areas of disease. "This is pie in the sky," he said, "but
at least there is now the possibility of thinking about it."
"After just five days
of non-invasive brain stimulation and a bit
of cognitive training, researchers at Oxford
University were able to enhance people's
high-level abilities, such as mental arithmetic
and manual calculations. And remarkably,
the effect lasts for months.
The discovery was made by scientists working at Oxford's Department of
Experimental Psychology, and it could lead to entirely new education
strategies. But more immediately, it could also help people with learning
disabilities or neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s or
Parkinson’s. We contacted the lead researcher to learn more."
Cranial electrical stimulation
(CES) may improve memory, attention and
focus; important studies are emerging on
the uses of mild electrical current to
enhance cognition and aspects of intelligence.
For those of you that still
think this is voodoo medicine, do a google
search for electroporation, electropharmacology
and cell biomembrane transport. Also do
a PUB MED search for Saul Liss, PhD, to
pull up actual abstracts
|
Dr William T Greenough, a neuroscientist at the University of Illinois, said
the Princeton work created a "whole new ball game" for addressing
brain diseases, by harnessing the brain's own restorative potential.
The Princeton biologists plan to follow up their discovery by blocking the
formation of new neurons in monkeys' brains and seeing what happens. If the
new neurons are essential for memory and learning, then serious deficits should
appear in the monkeys' performance. The researchers as yet have no idea whether
the loss of brain cells and the generation of new ones are separate events
or part of the same cycle.
"Our discovery," Dr Gross said, "suggests more questions than
answers."
BT
Pro Multi system
 Full
LED screen Full
LED screen
  Built
in frequencies Built
in frequencies
Delta
Brain Waves
 0.5
Hz Anxiety release 0.5
Hz Anxiety release
 1.5
Hz Deep sleep 1.5
Hz Deep sleep
 2.0
Hz Healing Of Nerves 2.0
Hz Healing Of Nerves
Theta
Brain Waves
 Deep
Theta 5.0 Hz Release Brain fog, retain
recall release information faster Deep
Theta 5.0 Hz Release Brain fog, retain
recall release information faster
 7.83
Hz Meditation 7.83
Hz Meditation
Alpha
Brain Waves
 10
Hz Cell Rejuvenation 10
Hz Cell Rejuvenation
More
Healing Frequencies
 15
Hz Lymph System Circulation 15
Hz Lymph System Circulation
 20
Hz Breast lumps 20
Hz Breast lumps
 35
Hz Stimulate Clarity of Thought, Mental Function 35
Hz Stimulate Clarity of Thought, Mental Function
 100.00
Hz Feeling Down 100.00
Hz Feeling Down
 500Hz
Chronic depression 500Hz
Chronic depression
 1434
Hz White Blood Cell stimulation 1434
Hz White Blood Cell stimulation
 1524
Hz Red Blood Cell Stimulation 1524
Hz Red Blood Cell Stimulation
 Plus
the Full BT6-BT11 Beck Protocol 1000.00 Hz
+ 111.00 Hz Plus
the Full BT6-BT11 Beck Protocol 1000.00 Hz
+ 111.00 Hz
 Over
700 Natural Harmonic frequencies Over
700 Natural Harmonic frequencies
 Fully
Rechargeable ...Batteries/Charger Fully
Rechargeable ...Batteries/Charger
 Timer
: 5 - 60 mins Timer
: 5 - 60 mins
 Intensity
Control Intensity
Control
 Very
portable Very
portable
 Instructions Instructions
 High
Quality Ear clips High
Quality Ear clips
 Tens
pads and lead Tens
pads and lead
 LCD
Screen LCD
Screen
 Many
more add on options Many
more add on options
|
Latest
BT Pro Master
Unit
Master unit

 Larger
Screen with more information Larger
Screen with more information
 16
bit Processor for faster more accurate settings 16
bit Processor for faster more accurate settings
 More
Amazing Add on Apps options More
Amazing Add on Apps options
 Very
durable case Very
durable case
 High
quality Ear clips High
quality Ear clips
 Basic
option (Master unit) with Bio-feedback
app Basic
option (Master unit) with Bio-feedback
app
|
Bio-feedback
App
There is a relationship between
Stress and the Electrical conductivity of
the skin. This is known as Galvanic Skin
Response or GSR. |
Free
Option allows one to measure GSR
Skin conducts electric current
like a Resistor. The resistance of Skin can
vary from 25 Kilo Ohms to 2 Mega Ohms depending
on the Emotional state (This varies from
person to person ).This variation is due
to the changes in the permeability of the
skin. In a normal fully relaxed person, skin
resistance will be around 2 Mega Ohms. This
is due to the low permeability of the skin.
Skin offers high resistance and restricts
the current flow. But if the same person
is in stress, his skin resistance reduces
to 25 Kilo Ohms or less due to leakage of
water from the blood vessels and subsequent
sweating. This increases the electrical conductivity
of the skin. Thus the electrical conductivity
of the skin and Stress are directly related
Bonus
App with BT Pro Unit |
Additional
Add on Apps.
Full Descriptions of ADD on Apps
Options Below !
|
|
Alzheimer's
Rife Frequency set

|
Unlocking
this App gives you
Alzheimer's Frequency set,
these are frequencies from our own long experience
and the works of many therapists world wide,
we don't offer any cures just practical experience
and knowledge Frequency
source
High Quality Ear clips come with the BTPro
 Unlock
code Unlock
code
 Add Alzheimer's
Rife Frequency App Add Alzheimer's
Rife Frequency App
Note: Only For BTpro
Ver 5 and up
|
|
Parkinson's
Rife Frequency App

|
Unlocking
this App gives you
(Click on
the links for interesting research)
Parkinson's Rife
Frequency set, these are frequencies from
the works of many therapists world wide,
we don't offer any cures just experience
and knowledge Frequency
source
it has been suggested by users that the
addition of the magnastim headset (below)
has greatly enhanced the effects of these
frequencies
High Quality Ear clips come with the BTPro
 Add Parkinson's
Rife Frequency App Add Parkinson's
Rife Frequency App
Note: Only For BTpro
Ver 5 and up
|
|
Diabetes
App

|
DIBT (Diabetes) 3 Frequency
sets
1, DIBT(Diabetes)
1Hz, 2, 6.8, 20, 35, 48, 95, 125, 72, 302,
440, 444, 465, 484,500, 660, 727, 787, 800,
802,803, 880, 1550, 1800, 1850, 1865, 2000,
2003, 2008, 2013, 2050,2127, 2128, 2080 ,2170,
2720, 4000, 4200, 5000, 10000, 32000 Hz Each
frequencyruns for 3 min , Hz
2, DBAI (Diabetes
associated infection) 2020, 800, 727, 190,
80, 20 Each frequencyruns for 3 min , Hz
3, DBLO (Diabetic
loading) 35, 700 Each frequencyruns for 3
min , Hz
4 PEMF Med Magnacoil and Adapter
5 Carbon silicon hand helds
6 Instructions
Note: Only For BTpro Ver
6 and up |
|
Mind
Wave
|
Unlocking
this Option gives you complete frequency
set
 Gamma 40
hz 50hz 60 hz 70 hz 80 hz Gamma 40
hz 50hz 60 hz 70 hz 80 hz
 Beta 14
hz 18hz 20hz 22hz 27hz 28hz 30hz Beta 14
hz 18hz 20hz 22hz 27hz 28hz 30hz
 Alpha 9
hz 10 hz 11 hz 12 hz 13 hz Alpha 9
hz 10 hz 11 hz 12 hz 13 hz
 Theta 4
nz 4.5 hz 5 hz 6 hz 7 hz 7.83 hz 8.0hz Theta 4
nz 4.5 hz 5 hz 6 hz 7 hz 7.83 hz 8.0hz
 Delta 0.5hz
1 hz 2 hz 3 hz 3.9 hz Delta 0.5hz
1 hz 2 hz 3 hz 3.9 hz
 Unlock
code Unlock
code
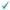 Add
Mind Wave option Add
Mind Wave option
Note: For Btpro Ver 2
and up
|
|
Magnastim
Option

CEF (Cranial electromagnetic fields) Stimulator
|
Unlocking
this App gives you the full potential of
the Magnastim
More Information
here
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these Unlock
code plus you will be sent these
 Magnastim
headset Magnastim
headset
 Magnastim
Driver Magnastim
Driver
 Now
has 528 DNA frequency Now
has 528 DNA frequency
 Add
Magnastim option Add
Magnastim option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
|
Eye
mate Option

|
The
use of micro current stimulation to help
eye problems
 Frequency
Specific Micro current Stimulator Frequency
Specific Micro current Stimulator
 Frequencies Frequencies
 5Hz,
292 Hz,, 292.7Hz ,30 Hz, 30.7Hz,,9.1 Hz 9.8Hz
and 0.3 Hz ,,10hz ,, 0.7 Hz,, 14Hz 1.5Hz,
3.6 Hz ,95hz 137 Hz, 18Hz 1.5hz, 3.6 hz 137Hz
1Hz 5Hz,
292 Hz,, 292.7Hz ,30 Hz, 30.7Hz,,9.1 Hz 9.8Hz
and 0.3 Hz ,,10hz ,, 0.7 Hz,, 14Hz 1.5Hz,
3.6 Hz ,95hz 137 Hz, 18Hz 1.5hz, 3.6 hz 137Hz
1Hz
 Each
frequency will run for aprox 24 sec. Each
frequency will run for aprox 24 sec.
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent Unlock
code plus you will be sent
 Eye
mask with silicon carbon contacts Eye
mask with silicon carbon contacts
 More
information and pictures here More
information and pictures here
 Add
Eyemate option Add
Eyemate option
Note: For Btpro Ver 2
and up
|
|
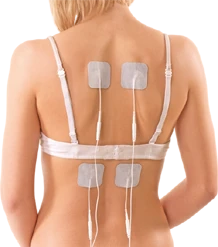
TENS
Option
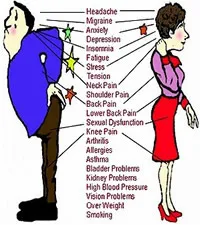
• Pain - from migraine
headaches . troubled feet ?
• Arthritis, Rheumatism, Muscle Spasms ?
• Backache - Sciatica, Neck and Shoulder complaints, trauma ?
• Circulatory System - peripheral circulation problems ?
• Respiratory disorders - Hay Fever, Sinusitis, Bronchial spasm, ?
• Inflammation - Burns, Bruising, Lesions, Bed Sores, Ankle Joint Swelling
?
• Tendonitis - R.S.I., bursitis, ligament and muscle strains, ?
• Sports Injuries - Acute, Cramps (relief of), also pre-sport and 'pre-exercise
toning ? |
Unlocking
this Option gives you the full potential
of the TENS
More information
here
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: Unlock
code plus you will be sent these:
 Lead
and two TENS pads Lead
and two TENS pads
 Lead
and 4 TENS Pads Lead
and 4 TENS Pads
 Add
TENS option Add
TENS option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
|
Sacred
harmony Option
Bring a little Miracle into
your Life
There is a special sound and color of love
according to Dr. Horowitz, a Harvard-trained
award-winning investigator. Broadcasting
the right frequency can help open your heart,
prompt peace, and hasten healing. "We
now know the love signal, 528 Hertz, is among
the six core creative frequencies of the
universe because math doesn't lie, the geometry
of physical reality universally reflects
this music
|
Unlocking
this Option gives you the full potential
of the Sacred Harmony functions
Built in Frequencies
 396
Hz -Red- Liberating Guilt and Fear 396
Hz -Red- Liberating Guilt and Fear 417
Hz - Orange - Undoing Situations and Facilitating
Change 417
Hz - Orange - Undoing Situations and Facilitating
Change
 528
Hz - Gold - Love Transformation and Miracles
(DNA Repair) 528
Hz - Gold - Love Transformation and Miracles
(DNA Repair)
 639
Hz - Green - Connecting/Relationships 639
Hz - Green - Connecting/Relationships
 741
Hz - Blue - Awakening Intuition 741
Hz - Blue - Awakening Intuition
 852
Hz - Purple - Returning to Spiritual Order 852
Hz - Purple - Returning to Spiritual Order
 Bonus
plus the 7.83 hz - Schumann Resonance frequency Bonus
plus the 7.83 hz - Schumann Resonance frequency
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: Unlock
code plus you will be sent these:
 Sacred
Harmony Coil and Lead Sacred
Harmony Coil and Lead
 Sacred
Harmony coil Driver Sacred
Harmony coil Driver
 Each
Sacred Harmony can be played individually
or as a sweep of PEMF More
Information Here Each
Sacred Harmony can be played individually
or as a sweep of PEMF More
Information Here
 Add
Sacred Harmony option Add
Sacred Harmony option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
|
Chakra
balance Option
Which uses the powerful Magnetic fields
of the Reiki Practitioner and the Vibrational
frequencies of Crystal Therapies
 7
Built in Chakra Frequencies 7
Built in Chakra Frequencies
 Powerful
Pulsed Magnetic Fields Powerful
Pulsed Magnetic Fields
 Run
Chakra frequencies Individually or Run
Chakra frequencies Individually or
 Ramp
the Seven for total Balance Ramp
the Seven for total Balance
|
Unlocking
this Option gives you the full potential
of the Chakra
balance
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these Unlock
code plus you will be sent these
 Chakra
balance Coil and Lead Chakra
balance Coil and Lead
 Chakra
balance Coil Driver Chakra
balance Coil Driver
The Chakra system functions as a map of
one’s evolutionary challenges (Ballentine,
1999). Each Chakra contains a spiritual life-lesson
that we must master in our evolution towards
higher consciousness.
More information
here
Built in Frequencies
 1st
Root/Muladhara - 194.18 Hz 1st
Root/Muladhara - 194.18 Hz
 2nd
Sacral/Svadhisthana -210.42 Hz 2nd
Sacral/Svadhisthana -210.42 Hz
 3rd
Solar Plexus/Manipura 126.22 Hz 3rd
Solar Plexus/Manipura 126.22 Hz
 4th
Heart/Anahata - 136.10 Hz ( OM ) 4th
Heart/Anahata - 136.10 Hz ( OM )
 5th
Throat/Vishuddha - 141.27 Hz 5th
Throat/Vishuddha - 141.27 Hz
 6th
Third Eye/Ajna - 221.23 Hz 6th
Third Eye/Ajna - 221.23 Hz
 7th
Crown/Sahasrara - 172.06 Hz 7th
Crown/Sahasrara - 172.06 Hz
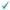 Add Chakra
balance option Add Chakra
balance option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
|
Sleepmate
Option
What would you do to feel good and get a
better night’s sleep???????
Difficulty falling or staying asleep is a common problem. About half
of Americans report sleep difficulty at least occasionally, according
to National Sleep Foundation surveys. These woes - called insomnia by
doctors - have far-reaching effects: a negative impact on concentration,
productivity and mood. Most of us don't know much about sleep, not even
our own and to make it worst ---- sleep problems have a profound effect
on our sleeping and waking life. |
Unlocking
this Option gives you the full potential
of the SleepMate
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: Unlock
code plus you will be sent these:
 Sleepmate
Coil and Lead+ Sleepmate
Coil and Lead+
 Sleepmate
Driver Sleepmate
Driver
 |
Catnap Takes you down into
Delta holds you there for 10 mins then
brings you back up |
 |
Sleep Takes you down to 5hz then lets
your drop off naturally |
 |
Insomnia Takes you way down to 0.05
hz very low delta your body will do the
rest |
 |
Wake up Feeling Drowsy need to wake
up, become more alert |
More
information here
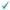 Add Sleepmate option Add Sleepmate option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
|
Bob
Beck Zapper Option
Dr Bob Beck obtained national attention
during the 1990's for his health-expo lectures
and public exposition of a healing protocol
known as "bioelectrification" or "blood
electrification", a simple electronic
therapy that was discovered to stop the replication
of the virus that causes AIDS.
|
Unlocking
this function gives you the full potential
of the Bob
Beck Blood Zapper
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: Unlock
code plus you will be sent these:
 Silver
Contacts Silver
Contacts
 Wrist
strap, Cotton Sleeves Wrist
strap, Cotton Sleeves
 Saline
Bottle Saline
Bottle
Subsequently, Bob discovered that many other
serious health conditions, including malaria,
responded favorably to blood electrification.
Many thousands, perhaps hundreds of thousands,
of people, worldwide, have benefited enormously
from the use of blood electrification due
to the lecturing efforts of Robert C. Beck.
Understanding
Blood Electrification
 Add Bob
Beck Zapper option Add Bob
Beck Zapper option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
|
Option
Colloidal silver Generator

Pennies-per-gallon, self-made perfected
colloids greatly assist in eliminating all
known pathogens and preventing opportunistic
infections. This has been known for a long
time.
Reported
Uses of Colloidal Silver |
Unlocking
this function gives you the full potential
of the Colloidal
Silver Gen
 Unlock
code, plus you will be sent these: Unlock
code, plus you will be sent these:
 Pair
of 99.9% silver wires plus leads Pair
of 99.9% silver wires plus leads
 Scourer
for cleaning silver rods Scourer
for cleaning silver rods
Home-made, pennies-per-gallon colloidal
silver acts as a "second immune system" according
to Bob Beck. It has been shown in numerous
studies to be the only substance known to
eliminate hundreds of viruses, bacteria,
fungus, etc.,
 Add colloidal
silver option Add colloidal
silver option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
|
Life
Stim Pro option

|
Unlocking
this function gives you the full potential
of our Famous LifeStim
option "Rife on your wrist"
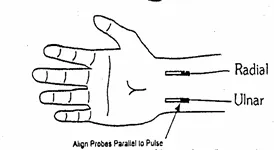
The "LifeStim", transmits 270+
of the best known Royal Rife, Bob Beck, John
Crane, Hulda Clarks,,tumor, parasite Candida
fungus Lyme and detox frequencies / harmonics
etc directly to the two arteries in the wrist,,for
as long as you wish to wear it. The option
is an amazing addition for any Rife machine
users, or detox parasite protocols,,this
unit allow the most effective frequencies
we have used to be run 24/7 if so desired.
 Unlock
code, plus you will be sent : Unlock
code, plus you will be sent :
 Tens
pads and leads for the wrist Tens
pads and leads for the wrist
More information
on the frequencies and application
Note: For Btpro Ver 4 and
up
|
|
Alpha
Mind Option
|
Unlocking
this function gives you the full potential
of the Alpha mind set of programs
1 AlphaStim slowly
takes you down to an Alpha mind state then
then after awhile slowly brings you back
up
2 ThetaStim slowly
takes you down to a Theta mind state then
after awhile slowly brings you back up
3 Lucid
Dreaming This program
takes one down into the possible lucid
dreaming mind frequencies
 Unlock
code, for all three programs: Unlock
code, for all three programs:
 To
be used with existing ear clips,supplied with
the Btpro v4 To
be used with existing ear clips,supplied with
the Btpro v4
Note: For Btpro Ver 4 and
up
|
|
|
Hulda
Clark type Option: Fully Auto Super sweep
frequency zapper
More |
Unlocking
this function gives you the full potential
of the Hulda
Clark type: Super sweep frequency zapper
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: |
 Copper
Hand holds Copper
Hand holds |
 Sweeps
up and down the 26khz -34khz range, Sweeps
up and down the 26khz -34khz range,
 Sweeps
up and down the 2.3-2.7khz range Sweeps
up and down the 2.3-2.7khz range
 Can
sweep both ranges separately Can
sweep both ranges separately
 Can
sweep both ranges consecutively, complete coverage Can
sweep both ranges consecutively, complete coverage
 Auto-timer
on Mode (7 minutes on, 20 minutes Pause, 7min
on, 20min Pause,, 7min on,20min Pause, 7min
on) Auto-timer
on Mode (7 minutes on, 20 minutes Pause, 7min
on, 20min Pause,, 7min on,20min Pause, 7min
on)
 Copper
Hand held Copper
Hand held
 Instructions
for use Instructions
for use
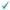 Add HC
Zapper option Add HC
Zapper option
Note: For Btpro All Versions |
Tinnitus

More |
Unlocking
this function gives you the full potential
of the Tinnitus
frequencis
 Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: Unlock
code plus you will be sent these: |
 Special
CES ear electrodes Special
CES ear electrodes |
 3
frequence sets , 3
frequence sets ,
 Tinnitus Tinnitus
 Hearing Hearing
 Meniere's
dis_ease Meniere's
dis_ease
 Special
Ear Elecrodes Special
Ear Elecrodes
 Instructions Instructions
 Add Tinnitus
frequency set Add Tinnitus
frequency set
Note: For Btpro Version
8 only release date 30-05-2020 |
|
The
Transend Broadcast Option
Send your Rife, Btpro, Earth or Sacred harmony
frequencies around your home or office.

|
Compatible with
Rife Pro all Models
BTPro
BTPlus
BT11
Schumann Shield
Harmony
Easy Plug & Play
AA Batteries (not included)
 Instructions
for use Instructions
for use
|
|
|
Special
Offer Save
Latest
BTpro v8 and all add ons
BTPro
Main Master unit with all functions activated,
 Bio
feed back, Bio
feed back,
 Sacred
Harmony Sacred
Harmony
 Headset
Driver and Power pack, Headset
Driver and Power pack,
 TENS
Function, TENS
Function,
 Sleep
mate, Sleep
mate,
 Bob
Beck Blood Zapper, Bob
Beck Blood Zapper,
 Chakra
Balancer, Chakra
Balancer,
 Magnastim, Magnastim,
 Hulda
Clark Zapper. Hulda
Clark Zapper.
 Colloidal
Silver Gen Colloidal
Silver Gen
 Eyemate Eyemate
 Mind
Wave Mind
Wave
 LifeStim
Option LifeStim
Option
 Alphamind
Option Alphamind
Option
 Parkinsons
option Parkinsons
option
 Alzheimers
option Alzheimers
option
 Transend Transend
 Tinnitus
option Tinnitus
option
 Diabetes
option Diabetes
option
 LED
Helmet LED
Helmet
All units use rechargeable
batteries (included),,and the charger is
sent for the voltage of your country
btprocom
|
Frequency
Comparison Chart
|

