|
Researchers believe that through control
of the electrical charges in the air we breathe, our
moods, energy and health can be markedly improved.

Reprinted from Reader's Digest
Condensed from The Rotarian.
Robert O’Brian
One sweltering summer day in Philadelphia
a man sat before a small metal box resting
atop
a hospital file cabinet. It was plugged into an ordinary
wall socket. A doctor flipped a switch. Inside the box
a small fan whirred; the box hummed distantly, like a
high-tension wire, and gave off a faint, sweetish odor.
Soon the man felt alert, magical, refreshed, as though
he had been taking deep gulps of sparkling October air.
The doctor turned the machine off, switched on another
that looked just like it. The air grew quickly stale.
The man's head felt stuffy. His eyes smarted. His head
began to ache. He felt vaguely depressed and tired.
With this simple experiment, the scientist, Dr. Igho H. Kornblueh, of
the American institute of Medical Climatology, demonstrated the effect
that atmospheric ions can have on human beings. The first machine generated
negative ions; the second positive ions.
The air around us is filled with these
electrically charged particles. They are generated in
invisible billions by cosmic rays, radioactive elements
in the soil, ultraviolet radiation, storms, waterfall,
winds, the friction of blowing sand or dust. Every time
we draw a breath they fill our lungs and are carried
by the blood to our body cells. They appear to have a
lot to do with such varied things as our moods, why cattle
grow skittish before a storm, why rheumatic joints "tingle" when
the barometer falls, and how ants know in advance that
it's going to rain, in time to block their tunnels.

Pollen, Pollution
and Asthma
The ion count is always low in cities where there's precious little open
ground to generate them. Pollution makes a bad situation worse, since
it tends to deplete the negative ion count even more. The high pollen
count in certain parts of North America each fall cuts even further into
the negative ion count, since pollen has the same effect as dust. The
end result is that the total ion count in cities is always down to what
many scientists consider perilously low levels. As if that weren't bad
enough, the normal 5 - 4 ratio of positive ions to negative ions is distorted
so that people are, in a sense, victims
of positive ion poisoning
"In Britain two Oxford
University statisticians conducted a study among
100 victims of asthma, bronchitis, and hay fever
chosen at random from a list of people who had
purchased negative ion generators in the hope
that it would help their problems. In the end
their report was based on interviews with only
74 of the 100. They found that 18 of 24 asthmatics;
13 of 17 bronchitis sufferers; 11 of 12 hay fever
victims; and 6 of 10 people afflicted with nasal
catarrh reported that negative ion generators
had noticeably improved their condition. A few
claimed the generator had cured them." (1) |
Falling barometric pressure and hot, dry,
seasonal winds, such as the Alpine Fohn and the Rocky
Mountain Chinook, for example, pack the air with an excess
of positive ions. Not everyone is affected; healthy young
people swiftly adapt to the change. But countless others
are distressed. The aged come down with respiratory complaints,
aching joints; asthma sufferers wheeze and gasp; children
grow cranky and perverse; crime and suicide rates climb.
Indoor Air Pollution:
The Silent Killer
"Brazilian Hospitals
have commonly used ionizing devices for the treatment
of breathing problems, including allergies, following
a test involving 36 children with asthmatic allergies.
All of them had consistent and in some cases
crippling problems before taking negative ion
therapy; during the treatment only one of them
suffered an allergy attack and afterward all
were reportedly cured, at least to the point
that they no longer suffered problems so long
as they took part in occasional negative ion
therapy sessions." (1) |
On the other hand, a preponderance of negative
ions spices the air with exhilarating freshness. We feel
on top of the world. Dr. C. W. Hansell, research fellow
at RCA Laboratories and an international authority on
ionization, illustrates the effect with a story about
his ten-year-old daughter. "We were outside, watching
the approach of a thunderstorm. I knew that clouds of
negative ions were filling the air. Suddenly my daughter
began to dance across the grass, a radiant look in her
face. She leaped up on a low boulder, threw her arms
wide to the dark sky, and cried. 'Oh, I feel wonderful!'"
Humidity
and Asthma
In humid areas - New York in
high summer, for instance, or in Toronto -
part of the familiar discomfort is caused by
the fact that air becomes ion-depleted. Really
humid days are murder for anyone suffering
from asthma or any respiratory allergy, and
the fact that such people find it difficult
to breath in hot, humid air may have less to
do with the amount of oxygen in the air then
with the massive negative ion depletion. Air
electricity is quickly conducted to the ground
by the moisture in the air, and what negative
ions there are attach themselves to particles
of moisture and dust and lose their charge.
We have seen how positive ions make breathing
more difficult and reduce the body's ability
to absorb oxygen; and how negative ions help
breathing and improve oxygen absorption. (1) |

At the University of Pennsylvania's Graduate Hospital
and at Northeastern and Frankford hospitals in Philadelphia,
Dr. Kornblueh and his associates have administered negative-ion
treatments to hundreds of patients suffering from hay
fever or bronchial asthma. Of the total, 63 percent have
experienced partial to total relief. "They come
in sneezing, eyes watering, noses itching, worn out from
lack of sleep, so miserable they can hardly walk," one
doctor told me. "Fifteen minutes in front of the
negative-ion machine and they feel so much better they
don't want to leave."

According to the latest information
in the fields of medicine, biology and meteorology,
it can be definitively established that atmospheric
ions have a biological effect. Atmospheric electrical
factors are a component of our environment and
we humans are clearly affected by electro-ionic
microclimates to a far greater extent than previously
imagined.
This finding acquires particular
significance since, as a result of artificial
air conditioning (e.g. atmospheric pollution,
buildings, air-conditioning units, heating,
electrical installations, plastics), civilized
man spends 50-100% of his time in an unnaturally
charged electroclimate. In cities, in closed
rooms and in cars, etc., the proportion of
small negative ions in the atmosphere is markedly
reduced compared with undisturbed nature.
Negative ions promote alpha
brain waves and increase brain waves amplitude,
which translates to a higher awareness level.
Those ion-induced alpha waves spread from the
occipital areas to the parietal and temporal
and even reach the frontal lobes, spreading
evenly across the right and left brain hemispheres.
All of this creates an overall clear and calming
effect, benefiting meditation and concentration. |
According to the latest information in
the fields of medicine, biology and meteorology, it can
be definitively established that atmospheric ions have
a biological effect. Atmospheric electrical factors are
a component of our environment and we humans are clearly
affected by electro-ionic microclimates to a far greater
extent than previously imagined.
This finding acquires particular significance since,
as a result of artificial air conditioning (e.g. atmospheric
pollution, buildings, air-conditioning units, heating,
electrical installations, plastics), civilized man spends
50-100% of his time in an unnaturally charged electroclimate.
In cities, in closed rooms and in cars, etc., the proportion
of small negative ions in the atmosphere is markedly
reduced compared with undisturbed nature.

Central
Air Conditioning and Heating
Hot or cool air forced through the duct work of most central heating
and air- conditioning systems sets up friction that results in
the loss of almost all the negative ions and also draws most of
the positive ions out of the air as well. Then comes the coup-de-grace:
This air with some positive and virtually no negative ions is forced
out through vents in to rooms, offices and passages - and as it
passes through the vents more friction is set up that generates
an additional overload of positive ions. What finally comes out
of most heating or air- conditioning outlets in the offices we
work in and the rooms we live in is likely to be an overload of
positive ions which will upset the mental and physical equilibrium
of everyone, not only those of us who are ion sensitive.
Just how bad these systems
are depends to a great extent on their design
and the material from which the duct work is
made. The design or layout of the whole system
is crucial. At bends and curves and right-angle
junctions the friction between ducts and air
increases and has the effect of increasing
the number of positive ions in the air. What
comes out of the heating and cooling vents
in any centrally heated or air-conditioned
building is air that is not only low in total
ions, but also has a heavy positive ion count
when measured against the almost negligible
quantity of negative ions. It is because of
the design of this duct work that some parts
of a building may be more "uncomfortable" to
work in then others. That depends on whether
you're on the receiving end of air that has
passed a particular section of duct work, where
there is a sharp bend near the outlet - as
the air is forced around bends and corners
there is greater friction and a consequent
increase in positive ions. |
It was RCA's Dr. Hansell who, in 1932,
stumbled upon the behavioral effects of artificially
generated ions. He notice a startling swing in the moods
of a fellow RCA scientist who worked beside an electrostatic
generator. Some days the scientist finished work alert
and in bubbling good spirits. On other days he was rude,
ill-tempered, depressed. Dr. Hansell investigated found
that the scientist was happy when the generator was adjusted
to produce negative ions, morose when it was producing
positive ions. A few months later, reports of ionization
research in Europe confirmed the strange experience.
"In 1966 at a hospital
in Jerusalem, doctors performed a series of tests
on thirty- eight infants between two and twelve
months old. All suffered to about the same degree
from respiratory problems. They were divided
into two groups of nineteen, one kept as a control
group in a ward without any ion charge and the
other where a negative ion generator was in use.
The researchers reported that
negative ions without any other treatment -
that is, no drugs - seemed to cure attacks
of asthma and bronchitis more quickly than
drugs, antibiotics included. They also observed
that there were none of the "adverse side
effects" frequently found when treating
such children with drugs. They concluded that
the children treated with negative ions were
less prone to "rebound attacks" (relapses).
As to objectivity, the scientific report said
that the tests "demonstrated that the
atmospheric ions have an effect on infants,
especially those suffering from asthmatic bronchitis." Less
scientifically, they found that babies didn't
cry as often and as loudly when they were breathing
negative ions as they did in normal air. And
there is nothing subjective about a bawling
baby." (1) |
A few years ago atmospheric ions became
suddenly important to military, researchers in environmental
medicine. How would they affect men locked in submarines?
In space ships? What were the possibilities of ions therapy?
Research programs multiplied, with fantastic results.
In Philadelphia Dr. Kornblueh studied brain-wave patterns
and found evidence that negative ions tranquilized persons
in severe pain. In one dramatic test he held a negative
ionizer to the nose and mouth of a factory worker who
had been rushed to Northeastern Hospital with second-degree
steam burns on his back and legs. In minutes the pain
was gone. Morphine, customarily administered in such
cases, was never necessary.
Considerable increase in
vital capacity were observed by M.A. Vytchikova
and A. Minkh in 1959, with the maintenance of
blood sugar and blood oxygen levels. Thus, in
a group of 9 sports students, Minkh found that
ergometer endurance was increased by 260% in
32 days compared with a normal control group
following the inhalation for 15 minutes daily
of air enriched with 1.5 million negative small
ions per centimeter. |
Today all burn cases at Northeastern are
immediately put in a windowless, ion conditioned room.
In ten minutes, usually, the pain has gone. Patients
are left in the room for 30 minutes. The treatment is
repeated three times every 24 hours. In 85 percents of
the cases no pain-deadening narcotics are needed. Says
Northeastern's Dr. Robert McGowan, "Negative ions
make burns dry out faster, heal faster and with less
scarring. They also reduce the need for skin-grafting.
They make the patient more optimistic. He sleeps better."
 |
Negative
Ions help us to sleep better.
In 1969, French researcher found that the overproduction of the
neurohormone serotonin caused sleeplessness and nightmares. In
using a negative ion electronic air cleaner to treat a group of
people experiencing sleeping problems as a result of serotonin
overproduction, he found that most of them were able to sleep better
(Soyka, 1991). |
Encouraged
by this success in burn therapy, Dr. Kornblueh, Dr. J.
R. Minehart, Northeastern's chief surgeon, and
his associate Dr. T. A. David boldly tried negative ions
in relief of deep, postoperative pain. During an eight
month test period they exposed 138 patients to negative
ions on the first and second days after surgery. Dr.
Kornblueh has just announced the results at a London
congress of bioclimatologists. In 79 cases 57 percent
of the total negative ions eliminated or drastically
reduced pain."At first," says Dr. Minehart, "I
thought it was voodoo. Now I'm convinced that it's real
and revolutionary."
The Director of the Danish
Air Ionization Institute, Christian Bach (electrical
engineer) has studied the clothes and environments
of asthmatics and others who suffer from positive
ion poisoning, then pinpoints the offending fabrics
and articles that are throwing the ion effect
out of balance. Bach and his colleagues have
worked with many hospitals in treating many victims
of asthma and other respiratory ills. |
Experiments by Dr. Albert P. Krueger and
Dr. Richard F. Smith at the University of California
have shown how ionization affects those sensitive to
airborne allergens. Our bronchial tubes and trachea,
or windpipe, are lined with tiny filaments called cilia.
The cilia normally maintain a whip like motion of about
900 beats a minute. Together with mucus, they keep our
air passages free of dust and pollen. Krueger and Smith
exposed tracheal tissue to negative ions, found that
the ciliary beat was speeded up 1200 a minute and that
mucus flow was increased. Doses of positive ions produced
the opposite effect: ciliary beat slowed to 600 a minute
or less; the flow of mucus dropped.

"The effect of ions
on respiration is more obvious. The U.S. experimenters
Windsor and Becket gave sixteen volunteer overdoses
of positive ions for just 20 minutes at a time
and all of them developed dry throats, husky
voices, headaches, and itchy or obstructed noses.
Five of the volunteers were tested for total
breathing capacity, and it was found that a positive
ion overdose reduced that capacity by 30 percent.
Exposed to negative ions for ten minutes , the
volunteers maximum breathing capacity was unaffected.
What is significant here is that negative ions
did not effect the amount of air breathed, but
positive ions made breathing more difficult. " |
In experiments that may prove important
in cancer research. Drs. Krueger and Smith also discovered
that cigarette smoke slows down the cilia and impairs
their ability to clear foreign, and possibly carcinogenic
(cancer-inducing), substances from the lungs. Positive
ions, administered along with cigarette smoke, lowered
the ciliary beat as before, but from three to ten time
faster than in normal air. Negative ions however, counteracted
the effects of the smoke. Observed Dr. Krueger, "The
agent in cigarette smoke that slows down the ciliary
beat is not known. Whatever it may be, its action is
effectively neutralized by negative ions, which raise
the ciliary beat as well in a heavy atmosphere of cigarette
smoke as they do in fresh air."

How do ions trip off our moods? Most authorities agree
that ions act on our capacity to absorb and utilize oxygen.
Negative ions in the blood stream accelerate the delivery
of oxygen to our cells and tissues, frequently giving
us the same euphoric jolt that we get from a few whiffs
of straight oxygen. Positive ions slow down the delivery
of oxygen, producing symptoms markedly like those in
anoxia, or oxygen starvation. Researchers also believe
that negative ions may stimulate the reticuloendothelial
system; a group of defense cells in our bodies which
marshal our resistance to disease.

Dr. Krueger predicts that we shall some day regulate
the ion level indoors much as we now regulate temperature
and humidity. Ironically, today's air-conditioned buildings,
trains and planes frequently become supercharged with
harmful positive ions because the metal blowers, filters
and ducts of air-conditioning systems strip the air of
negative ions before it reaches its destination. Says
RCA's Dr. Hansell, "This explains why so many people
in air conditioned spots feel depressed and have an urge
to throw open a window."

Air conditioner manufacturers are designing new systems
that increase negative ionization. The American Broadcasting
Co. will equip its new 30 story New York City headquarters
with ion control. Two national concerns, Philco and Emerson
Electric, already have ion control air conditioning systems
on the market. RCA, Westinghouse, General Electric and
Carrier Corp. have similar products under study or development.
BackgroundEpisodes of symptom complaints, including
upper and lower respiratory symptoms, eye and skin
irritation, headache, and fatigue, have been reported
for decades by occupants of office buildings in many
countries. Explaining and mitigating these problems
have been challenging. Numerous scientific studies
have documented that these building-related symptoms
(BRS), sometimes called sick building syndrome, are
surprisingly common even in buildings without widespread
health complaints (Burge, Hedge et al.
Risk Factors in Heating, Ventilating, and Air-Conditioning
Systems |
We still have much to learn about atmospheric ions .
But researches believe that these magic bits of electricity,
under artificial control, will soon be helping millions
to healthier, happier, more productive lives
Negative
Ions and Ozone Myths and Facts
Myth: "Ozone" and "Negative
ions" refer to the same thing.
Fact: Not so. They are very
different.
A negative ion is an oxygen atom with an extra electron. It is
odorless.
Ozone is an oxygen molecule consisting of three oxygen atoms. You
can smell ozone if the concentration is high enough.
Myth:
Ozone and negative ions perform exactly
the same functions in purifying the air.
Fact: The functions they perform are as different as night and
day. Sometimes both are needed to purify the air we breathe.
Negative ions rid the air of pollen, dust, etc.: stuff you can
see under a microscope. Ozone cannot. Negative ions also can improve
mood. Ozone cannot do that, either. Ozone gets rid of odors, pollutants,
etc.; stuff at the molecular level (although negative ions can
get rid of some odors, too.)
Myth:
Negative ions are nothing more than ordinary
static electricity.
Fact: That is a falsehood. Is there static electricity near waterfalls
or other areas where negative ions are naturally generated? Of
course not. Although some ionizers can induce a 'static' charge
on nearby objects under certain conditions, negative ions flow
through the air like electricity through a semiconductor.
Myth:
Negative ions can go through walls.
Fact: No way. Neither can ozone,
although ozone (if present) can go through heating
and cooling ductwork. Negative ions generally
cannot; they are attracted to the filter, air
conditioner evaporator coil (A-coil), and very
few emerge at furnace or air conditioning vents.
The exception is properly designed and placed
UV lamps, although they do not put as many negative
ions into the room as a good room ionizer.
Myth:
Too high a level of negative ions in the
room is bad for you.
Fact: Negative ions have not
been found to be harmful even in very high concentrations.
Just the opposite has been found the case. In
fact, there are patents using high-density negative
ions to treat depression.
Myth:
Ozone is ALWAYS a bad thing.
Fact: While ozone in extremely high concentrations is a toxic gas,
if the ozone level is properly selected, the ozone and the pollutants/odors
in the air CANCEL EACH OTHER. Overlooking this fact is the cause
of the ozone controversy we sometimes see. What is more, a little
ozone is often far preferable to the toxic gases and pollutants
it can eliminate from the air we breathe. |
Humidity
and Asthma
In humid areas - New York in high summer,
for instance, or in Toronto - part of the familiar discomfort
is caused by the fact that air becomes ion-depleted.
Really humid days are murder for anyone suffering from
asthma or any respiratory allergy, and the fact that
such people find it difficult to breath in hot, humid
air may have less to do with the amount of oxygen in
the air then with the massive negative ion depletion.
Air electricity is quickly conducted to the ground by
the moisture in the air, and what negative ions there
are attach themselves to particles of moisture and dust
and lose their charge. We have seen how positive ions
make breathing more difficult and reduce the body's ability
to absorb oxygen; and how negative ions help breathing
and improve oxygen absorption.
Heat is hard on the heart
Indoor Air Quality Dangers
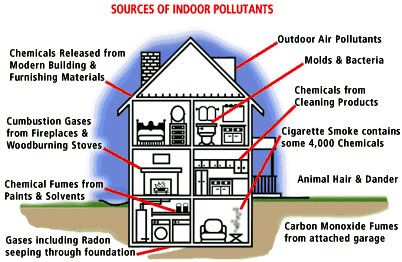
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) problems occur in buildings
where chemical and biological contaminants build up
to levels that can adversely affect some occupants. Source
|
At the University of Pennsylvania's Graduate Hospital
and at Northeastern and Frankford hospitals in Philadelphia,
Dr. Kornblueh and his associates have administered negative-ion
treatments to hundreds of patients suffering from hay
fever or bronchial asthma. Of the total, 63 percent have
experienced partial to total relief. "They come
in sneezing, eyes watering, noses itching, worn out from
lack of sleep, so miserable they can hardly walk," one
doctor told me. "Fifteen minutes in front of the
negative-ion machine and they feel so much better they
don't want to leave."

A few years ago atmospheric ions became suddenly important
to military, researchers in environmental medicine. How
would they affect men locked in submarines? In space
ships? What were the possibilities of ions therapy? Research
programs multiplied, with fantastic results.
In Philadelphia Dr. Kornblueh studied brain-wave patterns
and found evidence that negative ions tranquilized persons
in severe pain. In one dramatic test he held a negative
ionizer to the nose and mouth of a factory worker who
had been rushed to Northeastern Hospital with second-degree
steam burns on his back and legs. In minutes the pain
was gone. Morphine, customarily administered in such
cases, was never necessary.
Encouraged by this success in burn therapy, Dr. Kornblueh,
Dr. J. R. Minehart, Northeastern's chief surgeon, and
his associate Dr. T. A. David boldly tried negative ions
in relief of deep, postoperative pain. During an eight
month test period they exposed 138 patients to negative
ions on the first and second days after surgery. Dr.
Kornblueh has just announced the results at a London
congress of bioclimatologists. In 79 cases 57 percent
of the total negative ions eliminated or drastically
reduced pain."At first," says Dr. Minehart, "I
thought it was voodoo. Now I'm convinced that it's real
and revolutionary."

Experiments by Dr. Albert P. Krueger and Dr. Richard
F. Smith at the University of California have shown how
ionization affects those sensitive to airborne allergens.
Our bronchial tubes and trachea, or windpipe, are lined
with tiny filaments called cilia. The cilia normally
maintain a whip like motion of about 900 beats a minute.
Together with mucus, they keep our air passages free
of dust and pollen. Krueger and Smith exposed tracheal
tissue to negative ions, found that the ciliary beat
was speeded up 1200 a minute and that mucus flow was
increased. Doses of positive ions produced the opposite
effect: ciliary beat slowed to 600 a minute or less;
the flow of mucus dropped.

In experiments that may prove important in cancer research.
Drs. Krueger and Smith also discovered that cigarette
smoke slows down the cilia and impairs their ability
to clear foreign, and possibly carcinogenic (cancer-inducing),
substances from the lungs. Positive ions, administered
along with cigarette smoke, lowered the ciliary beat
as before, but from three to ten time faster than in
normal air. Negative ions however, counteracted the effects
of the smoke. Observed Dr. Krueger, "The agent in
cigarette smoke that slows down the ciliary beat is not
known. Whatever it may be, its action is effectively
neutralized by negative ions, which raise the ciliary
beat as well in a heavy atmosphere of cigarette smoke
as they do in fresh air."

How do ions trip off our
moods? Most authorities agree that
ions act on our capacity to absorb and utilize oxygen.
Negative ions in the blood stream accelerate the
delivery of oxygen to our cells and tissues, frequently
giving us the same euphoric jolt that we get from
a few whiffs of straight oxygen. Positive ions slow
down the delivery of oxygen, producing symptoms markedly
like those in anoxia, or oxygen starvation. Researchers
also believe that negative ions may stimulate the
body's defense systems.
Vitamins
of the Air?
Generally speaking, negative ions increase the flow of oxygen to
the brain; resulting in higher alertness, decreased drowsiness,
and more mental energy," says Pierce J. Howard, PhD, author
of The Owners Manual for the Brain: Everyday Applications from
Mind Brain Research and director of research at the Center for
Applied Cognitive Sciences in Charlotte, N.C.
"They also may protect
against germs in the air, resulting in decreased
irritation due to inhaling various particles
that make you sneeze, cough, or have a throat
irritation." |
Indoor Air Can Cause Health Problems
Are you worried about the air you breathe? Don't think
you're safe just because you're inside. The Environmental
Protection Agency (EPA) says that the air in homes and
other buildings can be more seriously polluted than the
outdoor air. Source
U.S. Dept.
of Agriculture
A recent study by the U.S. Dept. of
Agriculture found that ionizing a room led to 52% less
dust in the air, and 95% less bacteria in the air (since
many of the pollutants found in the air reside on floating
dust particles).

Agriculture Research Service (of USDA)
The Agriculture Research Service of the U.S. Dept. of Agriculture tested
the effectiveness of ionizers for removing dust in a poultry hatchery.
The dust level is very high in such an environment. In this study,
the use of an ionizer resulted in dust removal efficiencies that averaged
between 81.1 and 92.2%. The airborne transmission of salmonella (to
the eggs) was also significantly reduced as a result.
Journal of Applied Microbiology
The use of negative ions was even found
by scientists to reduce the presence of airborne viruses
by about 40%. A study featured in the 1987 issue also
showed the negative ions are free from any adverse side
effects

Don’t
travel to space without `em
Former NASA scientist James B. Beal, who came across the negative ion
problem while studying the type of environment needed in space capsules,
wrote: "The human race was developed in ionized air. Nature used
the ions in developing our biological processes." In other words,
people have been designed to function properly in an environment that
contains certain level of ionization (Soyka, 1991).

The more the better
Fred Soyka, author of "The Ion Effect" reports that based on
the 5,000 plus scientific documents that have been published regarding
negative ion studies, all support the conclusion that an overload of
negative ions seems to be beneficial (Soyka, 1991).
Sick building syndrome
The sick building syndrome comprises of various nonspecific
symptoms that occur in the occupants of a building. This
feeling of ill health increases sickness absenteeism and
causes a decrease in productivity of the workers. As this
syndrome is increasingly becoming a major occupational
hazard, the cause, management and prevention of this condition
have been discussed in this article. Source

click on picture for larger image
|
Heavy
duty high quality Real Car Air Ionizer

 Ion Output:
=12x 106/cm3 Ion Output:
=12x 106/cm3
|
|
Air ionizer, Air Cleaner
Features
• Super purification
• 15 million super-high concentration of negative
ions to clean indoor air
• With a built-in import material carbon cobalt alloy
stainless steel needle
• Ultra-low power
|
| |
Home
Office or Work space Ionisers
We must surround ourselves with sufficient
amount of negative ions,
these days, in order to ensure our heath and well-being |
| |
|
 |
Water Ozonator Negative
Ionizer Combo Unit
Ideal for purifying air, cleaning fish tanks,
removing airborne dust, smoke, mold, and pet odors,
purifying drinking water, and enriching oils for
skin therapy.
more information
|
| |
|
1 Advanced Research on Atmospheric Ions and Respiratory
Problems
by Guy Cramer
Sept. 2,1996
The majority of this report on Asthma and Ions was taken
directly form the book;
" The Ion Effect" by Soyka, Fred ( Lester and Orpen Limited, 1977)
these references can be found on pages 31, 35, 45, 56-57, 63, 75, 76, 77, 79-80,
84, 85, 90, 128, 129-131
|

